Demystifying the EGR Valve Position Sensor: Key to Engine Efficiency
1. Understanding the EGR System
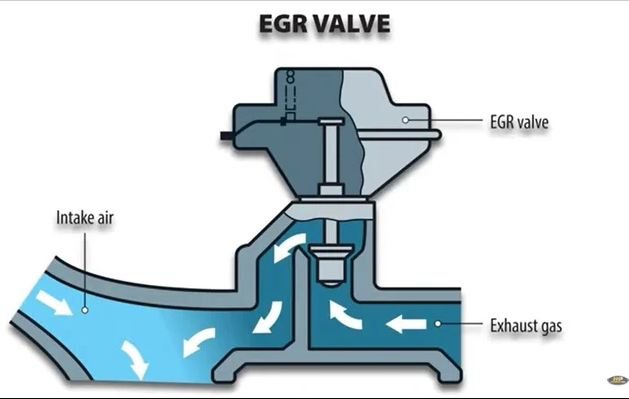
The Exhaust Gas Recirculation (EGR) system is a crucial component in modern vehicle engines. It works by recirculating a portion of the exhaust gases back into the combustion chamber, reducing nitrogen oxide emissions and improving fuel efficiency.
2. Introduction to the EGR Valve Position Sensor
Among the many components of the EGR system, the EGR Valve Position Sensor plays a pivotal role. This sensor is responsible for monitoring the position of the EGR valve, ensuring that it operates effectively within the engine’s parameters.
3. Importance of Monitoring and Maintaining the Sensor
Maintaining optimal performance of the EGR Valve Position Sensor is paramount for the efficient functioning of the EGR system as a whole. Failure to monitor and address issues with this sensor can lead to a cascade of problems, including decreased engine performance, increased emissions, and potential damage to other engine components.
Now, let’s delve deeper into the significance of the EGR Valve Position Sensor and why regular monitoring and maintenance are essential.
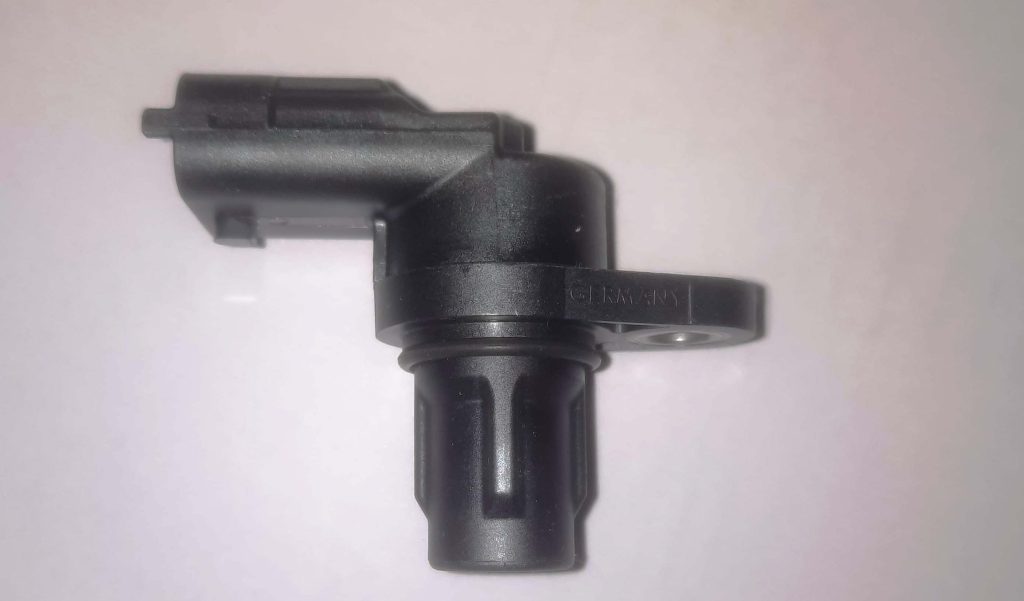
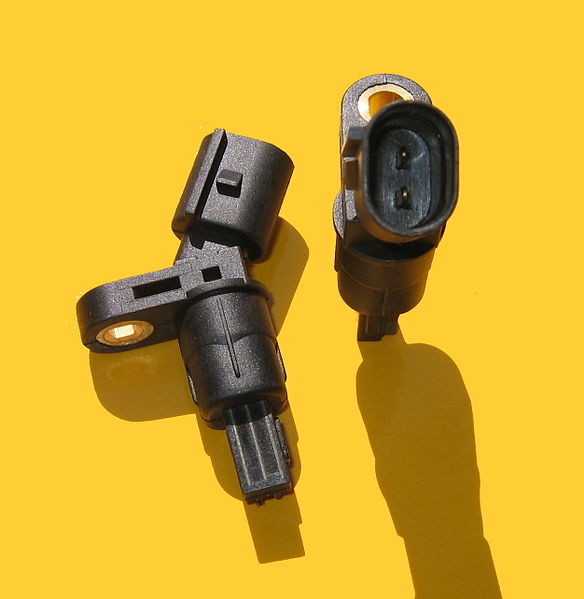
What is an EGR Valve Position Sensor?
The EGR Valve Position Sensor is a critical component within the Exhaust Gas Recirculation (EGR) system of an automobile. It serves the primary function of monitoring the position of the EGR valve, a key element in regulating exhaust gas flow into the combustion chamber.
Definition and Explanation
The EGR Valve Position Sensor is a sensor that detects and records the position of the EGR valve in an engine. It typically operates through a series of electronic signals, translating the physical movement of the valve into data that can be interpreted by the engine control unit (ECU).
Role within the EGR System
Within the EGR system, the EGR Valve Position Sensor acts as the eyes and ears, providing crucial feedback to the engine management system. It ensures that the EGR valve operates within specified parameters, opening and closing at the appropriate times to regulate the flow of exhaust gases into the intake manifold.
How it Detects the Position of the EGR Valve
The EGR Valve Position Sensor utilizes various methods to detect the position of the EGR valve accurately. One common approach is through the use of potentiometers or Hall effect sensors, which measure the rotational movement of the valve shaft. These sensors generate voltage signals proportional to the position of the valve, allowing the ECU to precisely control EGR flow based on engine operating conditions.
By accurately detecting the position of the EGR valve, the EGR Valve Position Sensor ensures optimal engine performance, fuel efficiency, and emissions control. It plays a crucial role in maintaining the delicate balance between combustion efficiency and environmental responsibility in modern vehicle engines.
Functionality of the EGR Valve Position Sensor
The EGR Valve Position Sensor operates as a vital component within the intricate network of sensors and actuators that regulate engine performance and emissions control. Understanding its functionality is key to appreciating its role in maintaining engine efficiency and compliance with environmental standards.
How the Sensor Works
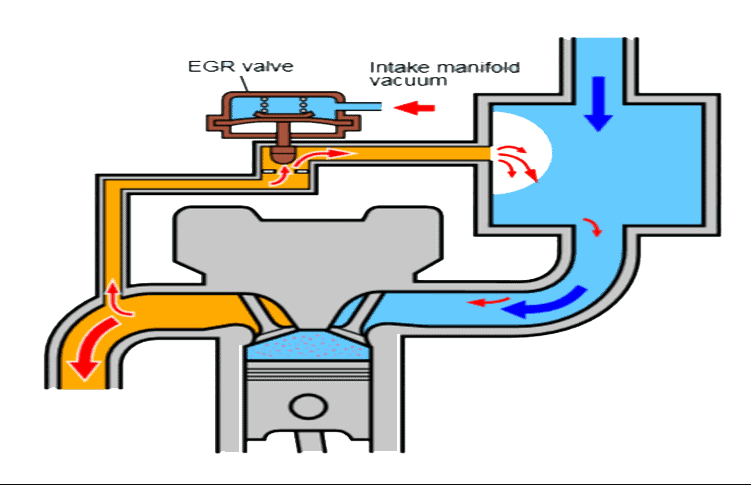
The EGR Valve Position Sensor operates on the principle of translating mechanical movement into electrical signals. As the EGR valve moves, either opening or closing, the sensor detects this movement and generates corresponding voltage signals.
This detection mechanism often relies on potentiometers or Hall effect sensors. Potentiometers measure the rotation of the valve shaft, while Hall effect sensors detect changes in magnetic fields caused by the movement of the valve. These sensors convert the mechanical motion into electrical signals, which are then transmitted to the engine control unit (ECU) for interpretation.
Signals Sent to the Engine Control Unit (ECU)
The signals generated by the EGR Valve Position Sensor are crucial for the ECU to make informed decisions about engine operation. These signals provide real-time feedback on the position of the EGR valve, allowing the ECU to adjust parameters such as fuel injection timing, air-fuel mixture, and ignition timing to optimize engine performance.
By continuously monitoring the position of the EGR valve, the ECU can precisely regulate the flow of exhaust gases into the intake manifold. This ensures that the engine receives the appropriate amount of recirculated exhaust gases to maintain combustion efficiency while minimizing harmful emissions.
Importance of Accurate Sensor Readings
Accurate readings from the EGR Valve Position Sensor are paramount for ensuring optimal engine performance and emissions control. Any deviation or malfunction in the sensor’s readings can lead to improper operation of the EGR system, resulting in issues such as reduced fuel efficiency, increased emissions, and potential engine damage.
Furthermore, inaccurate sensor readings can trigger diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs) and illuminate the check engine light, alerting the driver to potential problems with the EGR system. Regular maintenance and calibration of the EGR Valve Position Sensor are essential to prevent these issues and maintain the smooth operation of the vehicle.

EGR Valve Position Sensor plays a critical role in the functioning of the EGR system, providing essential feedback to the engine control unit for optimal engine performance and emissions control. Accurate sensor readings are vital for ensuring the efficient operation of the engine and minimizing environmental impact.
Importance of the EGR Valve Position Sensor
The EGR (Exhaust Gas Recirculation) system stands as a cornerstone of modern engine design, offering multifaceted benefits that extend beyond mere combustion efficiency. Within this system, the EGR Valve Position Sensor holds a pivotal role, facilitating the optimization of engine performance, emissions compliance, and fuel efficiency.
Crucial Role of the EGR System
The EGR system is indispensable for modern engines due to its ability to mitigate harmful emissions and enhance fuel efficiency. By recirculating a portion of exhaust gases back into the combustion chamber, the EGR system effectively reduces the formation of nitrogen oxides (NOx), a major contributor to air pollution. This technology not only helps vehicles meet stringent emissions regulations but also promotes environmental sustainability by curbing the release of harmful pollutants into the atmosphere.
Significance in Maintaining Emissions Compliance
The EGR Valve Position Sensor plays a crucial role in ensuring that the EGR system operates within regulatory limits. By accurately monitoring the position of the EGR valve, the sensor enables precise control over the flow of exhaust gases, facilitating optimal combustion conditions while minimizing emissions of NOx and other pollutants. This level of control is essential for vehicles to comply with increasingly stringent emissions standards imposed by regulatory agencies worldwide.
Impact on Fuel Efficiency and Engine Performance
In addition to emissions control, the EGR system, guided by the EGR Valve Position Sensor, significantly influences fuel efficiency and engine performance. By reintroducing exhaust gases into the combustion chamber, the system reduces peak combustion temperatures, thereby mitigating the formation of harmful pollutants and preventing engine knock. This results in smoother engine operation, improved fuel efficiency, and enhanced longevity of engine components.
Moreover, the precise monitoring and adjustment capabilities afforded by the EGR Valve Position Sensor enable the engine control unit to fine-tune engine parameters for optimal performance under varying operating conditions. This includes adjustments to air-fuel ratio, ignition timing, and turbocharger boost pressure, all of which contribute to maximizing engine efficiency and responsiveness.
EGR Valve Position Sensor is instrumental in harnessing the full potential of the EGR system, ensuring compliance with emissions regulations, optimizing fuel efficiency, and enhancing overall engine performance. Its role underscores the critical synergy between technology and environmental responsibility in the realm of automotive engineering.
Common Issues and Symptoms
The EGR Valve Position Sensor, like any other component in a vehicle, is susceptible to wear and malfunction over time. Recognizing the common issues and symptoms associated with this sensor is crucial for timely diagnosis and maintenance, preventing potential damage to the engine and ensuring continued performance and emissions compliance.
1. Overview of Common Problems
Several issues may arise with the EGR Valve Position Sensor, compromising its functionality and accuracy. These problems often stem from wear, electrical faults, or contamination within the sensor assembly. Common issues include:
- Sensor Malfunction: The sensor may fail to accurately detect the position of the EGR valve due to internal wear or electrical issues.
- Signal Interference: External factors such as dirt, debris, or moisture can interfere with the sensor’s signals, leading to erratic behavior or incorrect readings.
- Wiring Faults: Damaged or corroded wiring connections can disrupt communication between the sensor and the engine control unit (ECU), causing performance issues.
- Mechanical Wear: Components within the sensor assembly, such as potentiometers or Hall effect sensors, may degrade over time, affecting sensor accuracy and reliability.
2. Symptoms of a Failing or Faulty Sensor
Identifying the symptoms associated with a failing or faulty EGR Valve Position Sensor is essential for prompt diagnosis and repair. Common indicators of sensor issues include:
- Check Engine Light: The illumination of the check engine light on the vehicle’s dashboard may indicate a problem with the EGR system, including issues with the EGR Valve Position Sensor.
- Rough Idle: A rough or unstable idle may occur when the sensor fails to accurately regulate the flow of exhaust gases into the intake manifold, affecting engine combustion.
- Engine Performance Issues: Reduced power, hesitation, or stalling during acceleration may occur due to improper EGR valve operation resulting from sensor malfunction.
- Increased Emissions: Sensor failure can lead to elevated emissions of nitrogen oxides (NOx) and other pollutants, potentially causing the vehicle to fail emissions tests.
- Poor Fuel Efficiency: Inefficient EGR valve operation, resulting from sensor issues, can lead to decreased fuel efficiency and increased fuel consumption.
3. Potential Consequences of Ignoring Sensor Issues
Ignoring issues with the EGR Valve Position Sensor can have detrimental consequences for both vehicle performance and emissions compliance. These may include:
- Engine Damage: Continuous operation with a faulty sensor can lead to suboptimal engine performance, increased wear on engine components, and potential damage to the catalytic converter.
- Increased Emissions: Sensor issues may result in improper regulation of exhaust gas recirculation, leading to higher emissions of harmful pollutants and non-compliance with emissions regulations.
- Reduced Fuel Efficiency: Inefficient EGR valve operation, stemming from sensor malfunction, can result in decreased fuel efficiency and increased fuel consumption, ultimately impacting the vehicle’s operating costs.
In summary, recognizing the common issues and symptoms associated with the EGR Valve Position Sensor is crucial for maintaining optimal vehicle performance, emissions compliance, and fuel efficiency. Timely diagnosis and repair of sensor issues are essential to prevent potential engine damage and ensure continued reliability on the road.
VI. Diagnosing and Repairing EGR Valve Position Sensor Problems
Diagnosing and repairing issues with the EGR Valve Position Sensor requires a systematic approach to identify the root cause of the problem and implement appropriate solutions. Below are the steps involved in diagnosing sensor issues, techniques for testing the sensor’s functionality, and repair/replacement options for a malfunctioning sensor.
1. Diagnosing Sensor Issues
a. Scan for Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs): Begin by using an OBD-II scanner to retrieve any stored DTCs related to the EGR system or the EGR Valve Position Sensor. These codes can provide valuable insight into the nature of the problem.
b. Visual Inspection: Inspect the sensor and its wiring harness for any signs of physical damage, corrosion, or loose connections. Ensure that the sensor is securely mounted and that there are no obstructions interfering with its operation.
c. Functional Testing: Perform functional tests to assess the sensor’s response to changes in EGR valve position. This may involve manually operating the EGR valve while monitoring sensor readings using a multimeter or scan tool.
2. Testing the Sensor’s Functionality
a. Voltage Testing: Use a multimeter to measure the voltage output of the sensor while the engine is running. Compare the readings to specifications provided by the vehicle manufacturer to determine if the sensor is functioning within acceptable parameters.
b. Resistance Testing: If applicable, perform resistance testing on the sensor’s electrical circuitry to ensure that there are no open or short circuits. Refer to the vehicle’s service manual for specific resistance values and testing procedures.
c. Signal Verification: Verify that the sensor is sending consistent and accurate signals to the engine control unit (ECU) by monitoring live data using a scan tool. Look for any anomalies or erratic behavior that may indicate sensor malfunction.
3. Repair and Replacement Options
a. Cleaning and Calibration: In some cases, sensor issues may be resolved through cleaning and calibration. Remove the sensor from the vehicle and clean any dirt, debris, or carbon buildup that may be affecting its performance. Follow manufacturer recommendations for calibration procedures.
b. Repairing Wiring Faults: If the issue is related to wiring faults or connections, repair or replace damaged wiring harnesses as necessary. Ensure that all electrical connections are secure and free from corrosion.
c. Replacement: If the sensor fails to respond to testing or if it exhibits signs of irreversible damage or wear, replacement may be necessary. Replace the sensor with a new or refurbished unit that meets OEM specifications.
d. Professional Diagnosis: If diagnosing and repairing sensor issues prove challenging, consider seeking assistance from a qualified automotive technician or mechanic. They can perform advanced diagnostic procedures and recommend appropriate repair solutions.
Diagnosing and repairing problems with the EGR Valve Position Sensor involves a combination of visual inspection, functional testing, and, if necessary, repair or replacement. By following a systematic approach, drivers can effectively address sensor issues and restore optimal performance and emissions compliance to their vehicles.
Maintenance Tips
Proper maintenance of the EGR (Exhaust Gas Recirculation) system and its components, including the EGR Valve Position Sensor, is essential for ensuring optimal engine performance, emissions compliance, and longevity. Here are some guidance and best practices for maintaining the EGR system and extending the lifespan of the sensor:
1. Regular Inspection Intervals for the Sensor
a. Visual Inspection: Periodically inspect the EGR Valve Position Sensor and its wiring harness for any signs of damage, corrosion, or wear. Ensure that the sensor is securely mounted and that there are no obstructions interfering with its operation.
b. Functional Testing: Perform functional tests on the sensor to verify its response to changes in EGR valve position. Use diagnostic tools such as multimeters or scan tools to monitor sensor readings and ensure they fall within acceptable parameters.
c. Diagnostic Scans: Conduct diagnostic scans using an OBD-II scanner to check for any stored trouble codes related to the EGR system or the EGR Valve Position Sensor. Address any detected issues promptly to prevent further damage or malfunctions.
2. Maintenance of the EGR System and Components
a. Regular Cleaning: Periodically clean the EGR valve and its associated components to remove carbon deposits, dirt, and debris that can accumulate over time. Use a suitable solvent and a soft brush to clean the valve and its passages thoroughly.
b. Check for Clogging: Inspect the EGR passages for any signs of clogging or blockages that may restrict exhaust gas flow. Clean or unclog the passages as needed to maintain proper EGR system function.
c. Replace EGR Filter (if applicable): If your vehicle is equipped with an EGR filter, replace it at the recommended intervals to prevent buildup of contaminants and ensure efficient operation of the EGR system.
3. Best Practices for Extending Sensor Lifespan
a. Use Quality Parts: When replacing the EGR Valve Position Sensor, use high-quality OEM or aftermarket parts that meet or exceed manufacturer specifications. Avoid using cheap or inferior-quality parts that may fail prematurely.
b. Follow Manufacturer Recommendations: Adhere to the manufacturer’s recommended maintenance schedule for the EGR system and its components, including the sensor. Perform scheduled maintenance tasks such as cleaning, inspection, and replacement as outlined in the owner’s manual.
c. Avoid Harsh Driving Conditions: Minimize exposure to harsh driving conditions such as extreme temperatures, heavy loads, and prolonged idling, which can accelerate sensor wear and degradation. Drive responsibly and avoid aggressive driving habits that may strain the EGR system.
d. Keep Engine Well-Tuned: Maintain the overall health and performance of the engine by following recommended service intervals for oil changes, air filter replacement, and tune-ups. A well-tuned engine is less likely to experience issues with the EGR system and its components.
By following these maintenance tips and best practices, drivers can ensure the reliable operation of the EGR system and extend the lifespan of the EGR Valve Position Sensor, contributing to smoother engine performance, reduced emissions, and prolonged vehicle longevity.
EGR Valve Position Sensor Related Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs)
Certainly! When it comes to issues with the EGR Valve Position Sensor, there are several Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs) that may be related. These codes are logged in the vehicle’s onboard diagnostic system when the ECU detects abnormalities or malfunctions in the EGR system or its components. Here are some common DTCs related to EGR Valve Position Sensor problems:
- P0401 – Exhaust Gas Recirculation Flow Insufficient Detected: This code indicates that the ECU has detected insufficient flow in the EGR system, which may be caused by a malfunctioning EGR Valve Position Sensor among other factors.
- P0402 – Exhaust Gas Recirculation Flow Excessive Detected: Conversely, this code indicates that the ECU has detected excessive flow in the EGR system, which could also be attributed to issues with the EGR Valve Position Sensor.
- P0403 – Exhaust Gas Recirculation Control Circuit Malfunction: This code points to a problem with the electrical circuitry or wiring associated with the EGR Valve Position Sensor, indicating a potential issue with the sensor itself or its connections.
- P0404 – Exhaust Gas Recirculation Circuit Range/Performance: This code suggests that the EGR system is operating outside the expected range or performance parameters, which may be due to sensor malfunction or misalignment.
- P0405 – Exhaust Gas Recirculation Sensor A Circuit Low: This code indicates that the voltage signal from the EGR Valve Position Sensor is lower than expected, possibly due to a faulty sensor or wiring issue.
- P0406 – Exhaust Gas Recirculation Sensor A Circuit High: Conversely, this code indicates that the voltage signal from the EGR Valve Position Sensor is higher than expected, suggesting a potential sensor or wiring problem.
These are just a few examples of the DTCs that may be related to issues with the EGR Valve Position Sensor. It’s important to note that the specific codes and their meanings may vary depending on the make and model of the vehicle. If you encounter any of these DTCs or suspect problems with your EGR system, it’s recommended to consult with a qualified automotive technician for diagnosis and repair.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the EGR Valve Position Sensor stands as a critical component within the Exhaust Gas Recirculation (EGR) system, serving as the linchpin for optimal engine performance and emissions control. Throughout this article, we’ve underscored the importance of this sensor and its indispensable role in modern automotive engineering.
The EGR Valve Position Sensor plays a pivotal role in regulating the flow of exhaust gases into the intake manifold, thereby reducing harmful emissions and enhancing fuel efficiency. By monitoring the position of the EGR valve and providing crucial feedback to the engine control unit (ECU), this sensor ensures that the EGR system operates within specified parameters, maintaining the delicate balance between combustion efficiency and environmental responsibility.
It’s clear that the EGR Valve Position Sensor is not just another component in the engine bay; it’s a cornerstone of emissions control technology, integral to meeting stringent environmental regulations and promoting sustainable driving practices. Its proper monitoring and maintenance are essential for preserving engine performance, minimizing emissions, and ensuring the longevity of the vehicle.
As drivers and automotive enthusiasts, it’s incumbent upon us to recognize the significance of the EGR Valve Position Sensor and prioritize its care and maintenance. By adhering to recommended maintenance schedules, conducting regular inspections, and addressing any issues promptly, we can uphold the integrity of the EGR system and contribute to cleaner air, improved fuel efficiency, and a brighter automotive future.
In essence, the EGR Valve Position Sensor embodies the intersection of innovation, efficiency, and environmental stewardship—a testament to the ingenuity and dedication driving advancements in automotive technology. Let us remain vigilant in safeguarding this vital component, knowing that our collective efforts pave the way towards a cleaner, greener, and more sustainable automotive landscape.