Understanding P2003 DPF Damaged: Causes, Symptoms, and Solutions

P2003 DPF Damaged Error Code – Introduction
The P2003 error code specifically indicates an issue with the Diesel Particulate Filter (DPF). When this code appears, it signals that there’s a problem with the efficiency of the DPF, often due to blockages or damage. Understanding the implications of this error is crucial for maintaining the performance and longevity of your vehicle.
Importance of Addressing DPF (Diesel Particulate Filter) Issues Promptly
Addressing DPF issues promptly is essential for several reasons. Firstly, the DPF plays a vital role in reducing harmful emissions from diesel vehicles, contributing to cleaner air quality and environmental sustainability. Secondly, ignoring DPF problems can lead to decreased fuel efficiency and engine performance, potentially resulting in costly repairs down the line. Lastly, failure to address DPF issues promptly may result in the vehicle failing emissions tests, leading to legal and regulatory complications.
Preview of What the Article Will Cover
In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the intricacies of the P2003 DPF Damaged error code. From understanding its causes and symptoms to exploring effective diagnostic and repair strategies, this article aims to equip you with the knowledge needed to tackle DPF-related issues confidently. Additionally, we will discuss preventive maintenance measures to help you avoid encountering this error code altogether. Stay tuned as we unravel the mysteries surrounding the P2003 error code and empower you to keep your vehicle running smoothly.

What is P2003 DPF Damaged?
Definition of the P2003 Error Code
The P2003 error code is a diagnostic trouble code (DTC) that specifically indicates an issue with the Diesel Particulate Filter (DPF). It is often accompanied by a message indicating “DPF Damaged” or similar wording. When this code appears, it means that the efficiency of the DPF has fallen below the acceptable threshold, usually due to blockages or physical damage.
Explanation of DPF and Its Function in Diesel Vehicles
The Diesel Particulate Filter (DPF) is an essential component in modern diesel vehicles designed to reduce harmful emissions. It functions by trapping and storing particulate matter (soot) produced during the combustion process. The DPF then periodically goes through a process called regeneration, where the accumulated soot is burned off at high temperatures, leaving behind only ash. This process helps to maintain optimal performance and minimize environmental impact by reducing the emission of pollutants into the atmosphere.
Importance of Proper DPF Functioning for Vehicle Performance and Emissions Control
Proper functioning of the DPF is crucial for both vehicle performance and emissions control. From a performance perspective, a malfunctioning DPF can lead to decreased engine efficiency, reduced power output, and increased fuel consumption. Additionally, it can trigger other warning lights or error codes, further impacting the vehicle’s drivability.
Moreover, the DPF plays a significant role in emissions control by capturing and trapping harmful particulate matter before it is released into the air. Failure to address DPF issues promptly can result in higher emissions levels, contributing to air pollution and environmental degradation. Therefore, maintaining the proper functioning of the DPF is not only essential for preserving the performance of your vehicle but also for minimizing its environmental footprint.
Causes of P2003 DPF Damaged
Diesel Fuel Quality Issues
The quality of diesel fuel used in a vehicle can significantly impact the health and functionality of the Diesel Particulate Filter (DPF). Low-quality or contaminated diesel fuel may contain impurities and additives that can accelerate the accumulation of soot and ash in the DPF, leading to premature blockages and reduced efficiency. Additionally, high sulfur content in diesel fuel can increase the likelihood of sulfuric acid formation during the regeneration process, potentially causing damage to the DPF substrate.
Driving Habits and Conditions Affecting DPF Regeneration
The frequency and effectiveness of DPF regeneration depend on various driving habits and conditions. Short, stop-and-go journeys or prolonged idling can prevent the DPF from reaching the required temperature for effective regeneration, leading to incomplete combustion and soot buildup. Similarly, consistently driving at low speeds or in congested traffic can limit airflow through the exhaust system, impeding the regeneration process. Additionally, towing heavy loads or driving in hilly terrain may increase the load on the engine, affecting its ability to generate sufficient heat for regeneration.
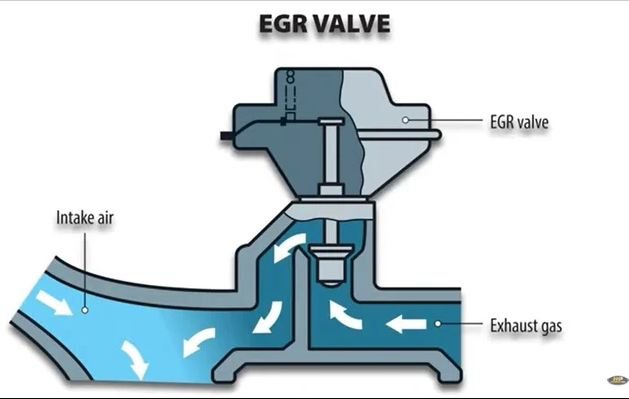
Faulty Sensors or Components Related to DPF System
The proper functioning of the DPF system relies on various sensors and components to monitor exhaust gas temperatures, pressure differentials, and other critical parameters. Faulty or malfunctioning sensors, such as the exhaust gas temperature sensor or differential pressure sensor, can inaccurately assess the condition of the DPF or hinder the regeneration process. Similarly, issues with components like the diesel oxidation catalyst (DOC) or selective catalytic reduction (SCR) system can indirectly affect DPF performance by altering exhaust gas composition or flow.
Engine or Exhaust System Malfunctions Contributing to DPF Damage
Underlying engine or exhaust system malfunctions can also contribute to DPF damage and inefficiency. Issues such as faulty fuel injectors, turbocharger malfunctions, or exhaust leaks can disrupt the combustion process, leading to increased soot production and DPF overload. Likewise, mechanical failures within the exhaust system, such as damaged exhaust pipes or mufflers, can affect exhaust gas flow and temperature regulation, impacting DPF regeneration and overall system performance. Identifying and addressing these root causes is essential for preventing recurring DPF issues and ensuring optimal vehicle performance.
Symptoms of P2003 DPF Damaged
Warning Lights or Messages on the Vehicle Dashboard
One of the most common and noticeable symptoms of a P2003 DPF Damaged error code is the illumination of warning lights or messages on the vehicle dashboard. This may include the Check Engine Light (CEL) or a specific DPF-related warning indicator. Additionally, some vehicles may display a message indicating “DPF Damaged” or a similar notification to alert the driver of a potential issue with the Diesel Particulate Filter.
Decreased Engine Performance or Responsiveness
A malfunctioning DPF can lead to decreased engine performance or responsiveness, affecting the vehicle’s acceleration, power output, and overall drivability. This can manifest as sluggish acceleration, reduced throttle response, or a noticeable decrease in engine power, especially during acceleration or when climbing hills. In severe cases, the vehicle may enter a limp mode, restricting performance to prevent further damage.
Increased Fuel Consumption
An inefficient DPF can also contribute to increased fuel consumption as the engine works harder to overcome reduced airflow and combustion efficiency. The accumulation of soot and ash in the DPF restricts exhaust flow, leading to higher backpressure in the exhaust system. This, in turn, can result in higher fuel consumption as the engine compensates for the decreased efficiency by consuming more fuel to maintain performance levels.
Unusual Noises or Smells from the Exhaust System
Damaged or clogged DPFs may produce unusual noises or smells from the exhaust system due to restricted airflow or incomplete combustion. This can include rattling or hissing sounds emanating from the exhaust, particularly during acceleration or regeneration cycles. Additionally, an overheating DPF may emit a distinctive burning odor as accumulated soot and particulate matter are incinerated during regeneration attempts.
Recognizing these symptoms is crucial for diagnosing and addressing DPF-related issues promptly. Ignoring these warning signs can lead to further damage to the DPF and other engine components, potentially resulting in costly repairs and decreased vehicle performance. Regular maintenance and timely intervention are essential for preserving the health and functionality of the DPF and ensuring optimal vehicle performance and emissions compliance.
Diagnosing P2003 DPF Damaged
Using OBD-II Diagnostic Tools to Retrieve Error Codes
The first step in diagnosing a P2003 DPF Damaged error code is to use OBD-II diagnostic tools to retrieve error codes stored in the vehicle’s onboard computer system. These tools can interface with the vehicle’s electronic control unit (ECU) to access diagnostic information, including DTCs (Diagnostic Trouble Codes) such as P2003. By retrieving and analyzing these codes, technicians can pinpoint the specific nature of the problem and identify potential causes.
Inspection of DPF and Related Components for Physical Damage
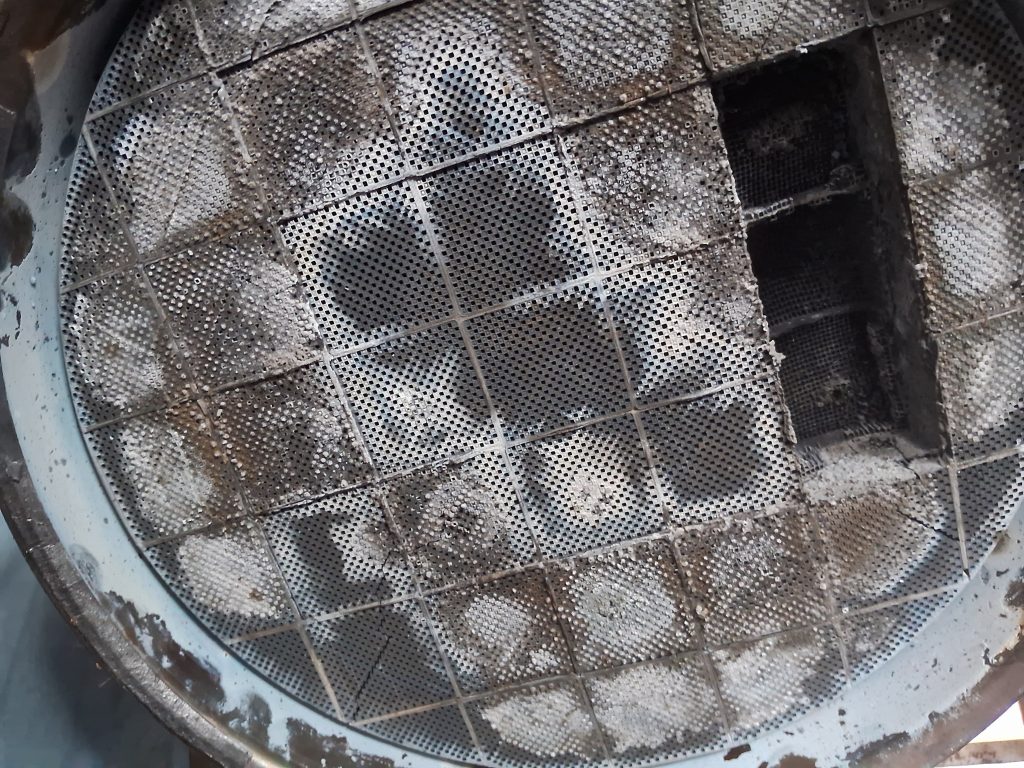
A visual inspection of the Diesel Particulate Filter (DPF) and related components is essential to assess for physical damage or signs of wear. Technicians will examine the DPF for cracks, leaks, or other visible defects that may indicate damage or deterioration. Additionally, they will inspect the DPF housing, exhaust pipes, and connections for signs of corrosion, impact damage, or loose fittings that could affect DPF performance.
Testing Sensors and Components for Proper Functionality
Testing the sensors and components related to the DPF system is critical for diagnosing P2003 DPF Damaged error codes accurately. This may involve using specialized diagnostic equipment to measure exhaust gas temperatures, differential pressure across the DPF, and other relevant parameters. Sensors such as the exhaust gas temperature sensor, differential pressure sensor, and oxygen sensors may be tested for proper functionality and calibration to ensure accurate readings.
Consultation with Automotive Professionals for Advanced Diagnostics if Needed
In cases where the diagnosis is complex or additional expertise is required, consultation with automotive professionals or specialists in diesel engine diagnostics may be necessary. Advanced diagnostic techniques, such as smoke testing, pressure testing, or dynamic testing under simulated driving conditions, may be employed to identify elusive or intermittent issues affecting DPF performance. Collaboration with experienced technicians or consulting with manufacturer service bulletins and technical resources can provide valuable insights into diagnosing and resolving P2003 DPF Damaged error codes effectively.
By following a systematic approach to diagnosing P2003 DPF Damaged error codes, automotive professionals can accurately identify the root cause of the problem and recommend appropriate repairs or corrective actions. This proactive approach helps to minimize downtime, reduce repair costs, and restore the vehicle to optimal performance and emissions compliance.
Solutions for P2003 DPF Damaged
Diesel Fuel System Maintenance and Cleaning
Regular maintenance of the diesel fuel system, including fuel filters and injectors, is crucial for preventing DPF issues related to fuel quality and contamination. Periodic fuel system cleaning and the use of high-quality diesel fuel can help minimize soot buildup and extend the lifespan of the DPF.
Driving Habits Adjustments to Promote DPF Regeneration
Modifying driving habits to facilitate DPF regeneration is essential for maintaining optimal DPF performance. This includes avoiding frequent short trips, maintaining consistent speeds on highways, and periodically driving at higher speeds to promote exhaust gas temperatures conducive to regeneration.
Repair or Replacement of Faulty Sensors or Components
Addressing issues with faulty sensors or components related to the DPF system is crucial for accurate monitoring and control of DPF regeneration. Repairing or replacing malfunctioning sensors, such as the exhaust gas temperature sensor or differential pressure sensor, can restore proper functionality and prevent recurring DPF error codes.
Engine and Exhaust System Repairs to Address Underlying Issues
Identifying and addressing underlying engine or exhaust system malfunctions is essential for preventing further damage to the DPF. Repairing issues such as faulty fuel injectors, exhaust leaks, or turbocharger malfunctions can improve engine performance and reduce soot production, alleviating strain on the DPF.
DPF Cleaning or Regeneration Procedures
Performing DPF cleaning or regeneration procedures is necessary to remove accumulated soot and ash from the filter and restore optimal DPF functionality. This may involve manual cleaning using specialized equipment or conducting regeneration cycles using diagnostic tools or vehicle-specific procedures.
Replacement of DPF if Damage is Severe or Irreparable
In cases where DPF damage is severe or irreparable, replacement may be the most viable solution. This typically involves removing the old DPF and installing a new or refurbished unit that meets OEM specifications. Proper installation and calibration are essential to ensure optimal performance and emissions compliance.
By implementing these solutions for P2003 DPF Damaged error codes, vehicle owners and automotive professionals can effectively address DPF-related issues and restore the performance and emissions compliance of diesel vehicles. Regular maintenance, proactive diagnostics, and timely repairs are key to minimizing downtime and maximizing the longevity of the DPF and associated components.
Prevention Tips for P2003 DPF Damaged
Regular Maintenance of Diesel Vehicles, Including DPF System Checks
Scheduled maintenance, including routine inspections of the Diesel Particulate Filter (DPF) system, is crucial for preventing P2003 DPF Damaged error codes. Regular checks of the DPF for signs of damage, soot accumulation, or leaks can help identify potential issues early and facilitate timely repairs or maintenance.
Using High-Quality Diesel Fuel from Reputable Sources
Choosing high-quality diesel fuel from reputable sources is essential for maintaining the health and efficiency of the DPF. Low-quality or contaminated diesel fuel can accelerate soot buildup and increase the risk of DPF blockages or damage. Opting for fuel with lower sulfur content and avoiding biodiesel blends can also help prolong the lifespan of the DPF.
Adhering to Recommended Driving Practices to Promote DPF Regeneration
Following recommended driving practices can help promote effective DPF regeneration and prevent the accumulation of soot and ash in the filter. This includes avoiding frequent short trips, maintaining consistent speeds on highways, and periodically driving at higher speeds to elevate exhaust gas temperatures. Additionally, minimizing idling and avoiding abrupt acceleration or deceleration can aid in DPF regeneration efforts.P2003
Prompt Addressing of Warning Signs or Error Codes Related to DPF Issues
Promptly addressing warning signs or error codes related to DPF issues is crucial for preventing further damage and ensuring optimal vehicle performance. Ignoring warning lights or messages on the vehicle dashboard can lead to increased fuel consumption, decreased engine performance, and potential emissions compliance issues. Consulting with automotive professionals and conducting thorough diagnostics at the first sign of trouble can help prevent more severe DPF-related problems down the line.
By incorporating these prevention tips into your maintenance routine and driving habits, you can proactively safeguard your diesel vehicle against P2003 DPF Damaged error codes and maintain the efficiency and longevity of the DPF system. Regular inspections, proper fuel selection, conscientious driving practices, and timely interventions are key to preventing DPF-related issues and preserving the performance and emissions compliance of your vehicle.
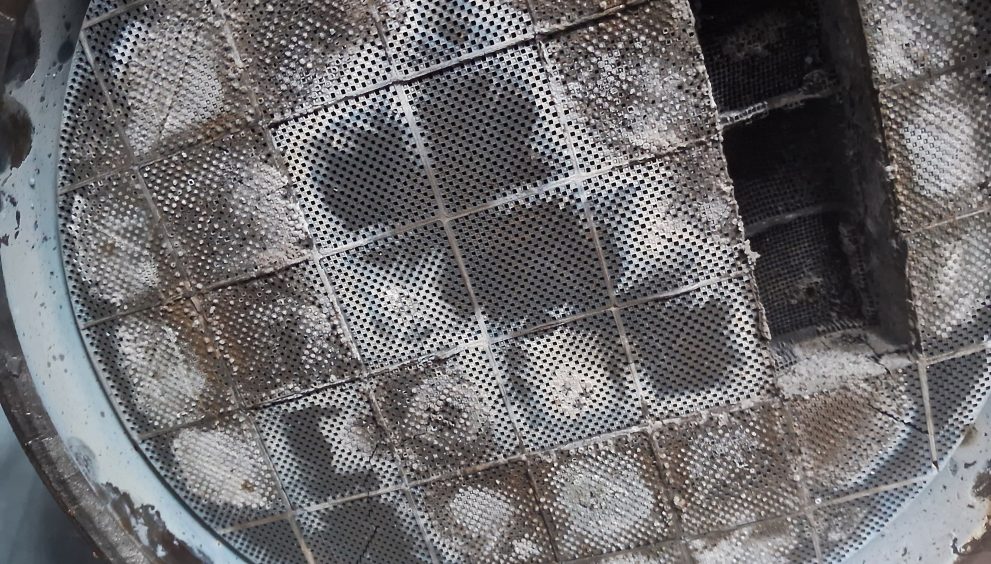
Damaged DPF Photos
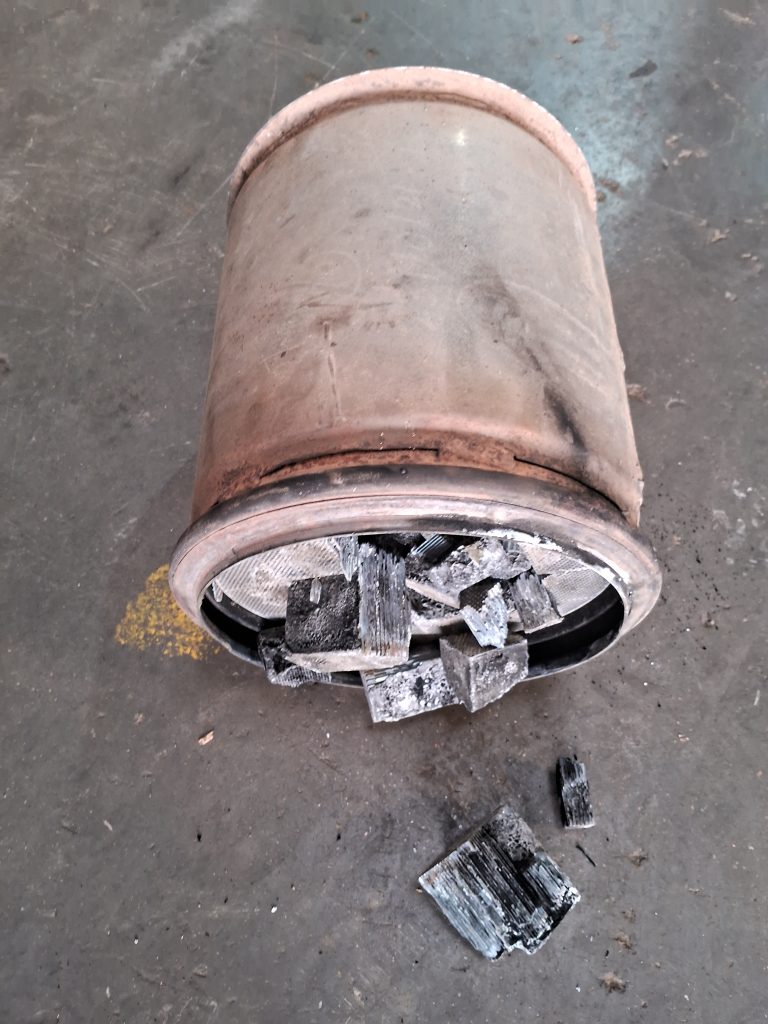
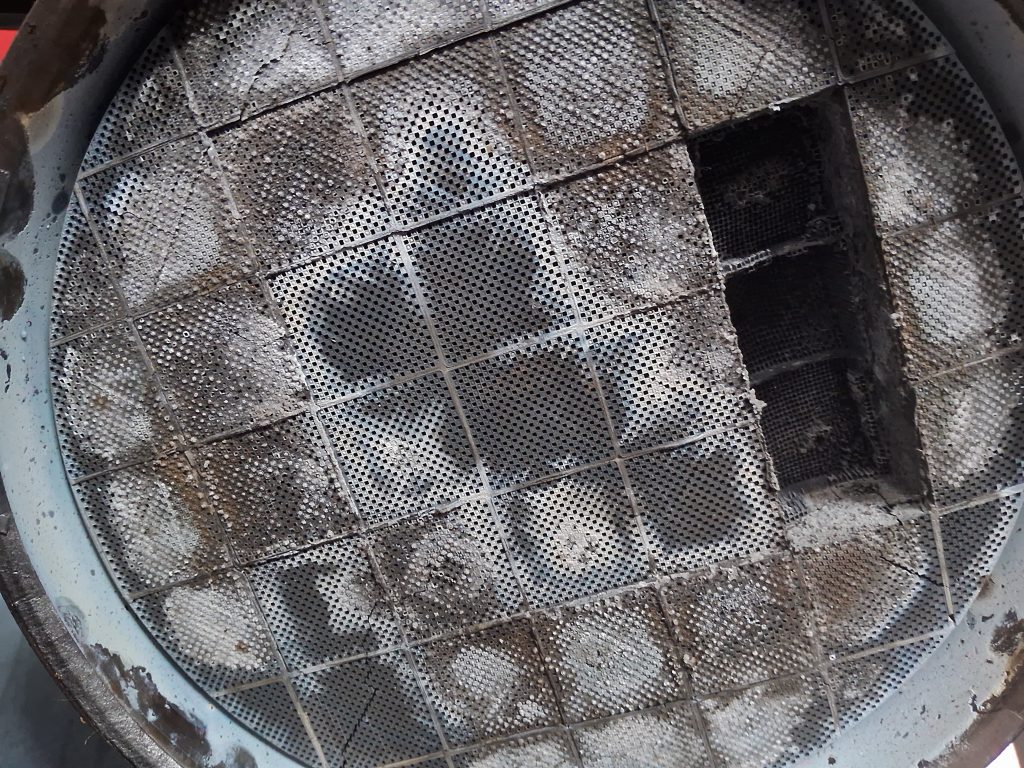
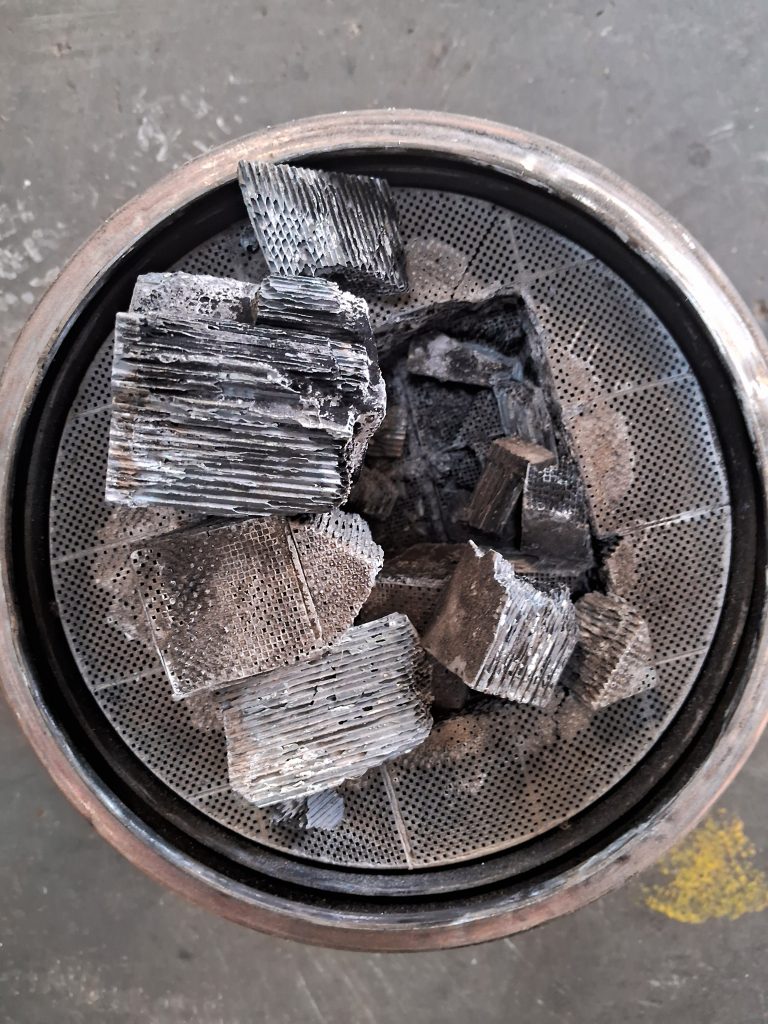
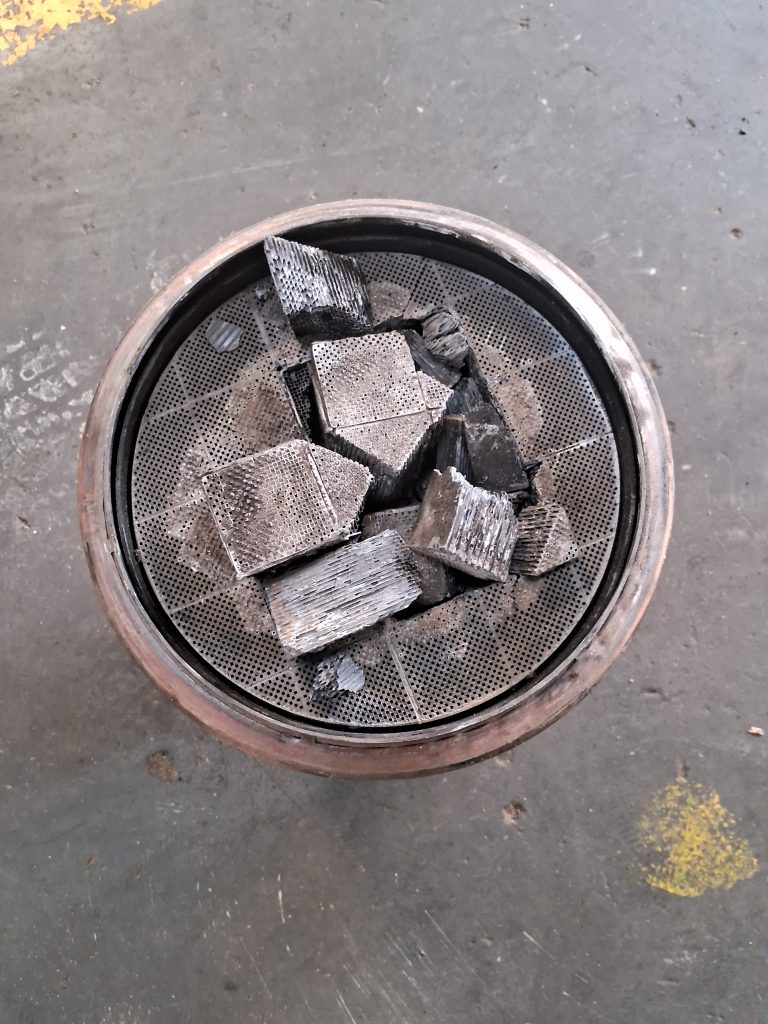




Conclusion – P2003 DPF Damaged error code
Throughout this article, we have explored the intricacies of the P2003 DPF Damaged error code, shedding light on its causes, symptoms, diagnosis, solutions, and prevention tips. We’ve discussed how this error code specifically indicates issues with the Diesel Particulate Filter (DPF) and highlighted the importance of maintaining proper DPF functionality for vehicle performance and emissions control.
Importance of Proactive Maintenance and Timely Repairs for DPF Health
Proactive maintenance and timely repairs are paramount for preserving the health and efficiency of the DPF system. Regular inspections, adherence to recommended driving practices, and prompt addressing of warning signs or error codes related to DPF issues can help prevent costly repairs and ensure optimal vehicle performance. By staying vigilant and proactive, diesel vehicle owners can extend the lifespan of their DPF and minimize the risk of encountering the P2003 DPF Damaged error code.
More Article Like- Understanding Code P244B: How to Deal with a DPF Clogged Error
Encouragement for Diesel Vehicle Owners to Stay Informed and Vigilant About DPF Issues
As the automotive industry continues to evolve, staying informed and vigilant about DPF issues is crucial for diesel vehicle owners. By staying abreast of the latest maintenance recommendations, diagnostic techniques, and regulatory requirements related to DPFs, owners can take proactive steps to protect their investment and contribute to cleaner air quality. Empowered with knowledge and awareness, diesel vehicle owners can confidently navigate the complexities of DPF maintenance and ensure the long-term health and performance of their vehicles.
In conclusion, addressing P2003 DPF Damaged error codes requires a multifaceted approach encompassing diagnostic expertise, maintenance diligence, and proactive intervention. By heeding the advice provided in this article and taking proactive measures to care for their DPF systems, diesel vehicle owners can enjoy peace of mind knowing that their vehicles are operating at peak efficiency while minimizing their environmental impact.