Understanding Code P244B: How to Deal with a DPF Clogged Error

Introduction – P244B DPF Clogged
In the realm of automotive diagnostics, few things are as crucial as understanding and promptly addressing error codes like P244B. This article delves into the significance of the P244B fault code and its implications for vehicle owners. Additionally, it sheds light on the critical role of Diesel Particulate Filters (DPF) in contemporary diesel engines, emphasizing the necessity of timely intervention when faced with a DPF clogged issue.
Understanding the P244B Error Code
The P244B error code is a diagnostic trouble code (DTC) that specifically relates to the functionality of the Diesel Particulate Filter (DPF) system in a vehicle. DTCs are generated by the onboard diagnostic (OBD) system of a vehicle when it detects a problem with a component or system. In the case of P244B, it signifies a restriction or blockage in the DPF’s regeneration process.
Exploring the Diesel Particulate Filter (DPF)
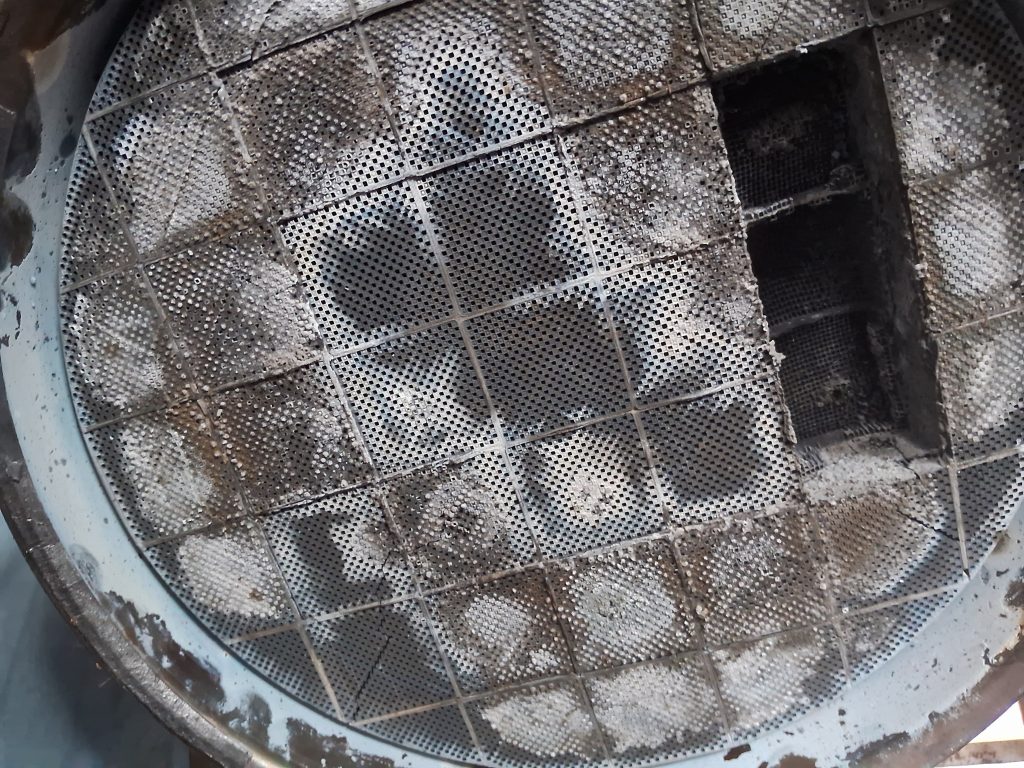
A Diesel Particulate Filter (DPF) is an integral component of modern diesel engines designed to reduce emissions of particulate matter, often referred to as soot, from the exhaust gases. It accomplishes this by trapping and then periodically incinerating particulate matter collected within the filter.
Importance of Timely Intervention
Promptly addressing a DPF clogged issue is paramount for several reasons. Firstly, a clogged DPF can lead to a decrease in engine performance and fuel efficiency. As the filter becomes obstructed, exhaust gases are unable to flow freely, resulting in reduced engine power and increased fuel consumption.
Secondly, ignoring a clogged DPF can cause further damage to the vehicle’s engine and emissions control system. Excessive back pressure from a blocked DPF can lead to increased stress on engine components and potentially result in costly repairs.
Moreover, failure to address a DPF clogged issue can lead to the activation of the vehicle’s limp mode, a safety feature that limits engine power to prevent further damage. This can significantly impede the vehicle’s drivability and may necessitate immediate attention from a qualified mechanic.
In conclusion, understanding the significance of the P244B fault code and the role of the DPF in modern diesel engines is crucial for vehicle owners. Timely intervention to address a DPF clogged issue not only preserves engine performance and fuel efficiency but also prevents potential damage to the vehicle’s engine and emissions control system.

Understanding P244B: Decoding the Error Code
The P244B error code is a crucial diagnostic indicator, particularly for diesel engine vehicles equipped with Diesel Particulate Filters (DPF). Let’s delve into a detailed exploration of what P244B signifies, how it’s generated, and the various factors contributing to its occurrence, especially in relation to DPF clogging.
1. What is P244B and its Relation to DPF Clogging?
P244B is a specific Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) that indicates a problem related to the operation of the DPF system. In simpler terms, it signals an issue with the DPF’s ability to effectively regenerate or clean itself, resulting in potential clogging. When the DPF becomes clogged, it obstructs the flow of exhaust gases, leading to decreased engine performance and increased emissions.
2. Generation of the Error Code by Onboard Diagnostics System:
The vehicle’s onboard diagnostics system continuously monitors various sensors and components to ensure optimal engine performance and emissions control. When it detects irregularities or malfunctions within the DPF system, such as insufficient regeneration activity or abnormal sensor readings, it triggers the generation of the P244B error code. This code serves as an alert to the driver and technicians that there is a problem that requires attention.
3. Factors Contributing to P244B Error:
Several factors can contribute to the occurrence of the P244B error code, with DPF clogging being a primary concern. Here are some key factors:
- Insufficient Regeneration Cycles: DPF regeneration is the process by which accumulated soot in the filter is burned off to maintain its effectiveness. If the vehicle primarily operates in conditions that do not allow for proper regeneration, such as short trips or low-speed driving, soot buildup can occur, eventually leading to clogging and the generation of the P244B error code.
- Faulty Components: Any malfunction or failure of components within the DPF system, such as the DPF pressure sensor, exhaust temperature sensor, or the DPF itself, can contribute to the occurrence of the P244B error. These components play a crucial role in monitoring and facilitating the regeneration process, and any discrepancies can lead to improper DPF function and subsequent clogging.
- Fuel Quality and Engine Maintenance: Poor fuel quality or inadequate engine maintenance can also indirectly contribute to DPF issues and the generation of the P244B error code. Contaminants in the fuel or engine oil can accelerate soot accumulation in the DPF, while engine malfunctions or misfires can disrupt the regeneration process, leading to clogging over time.
The P244B error code serves as a vital indicator of potential DPF clogging issues in diesel vehicles. Generated by the vehicle’s onboard diagnostics system, it highlights problems such as insufficient regeneration cycles or faulty components that require attention to prevent further damage and ensure optimal engine performance and emissions control.
Symptoms of a DPF Clogged Error: Recognizing the Signs
When a Diesel Particulate Filter (DPF) becomes clogged, it can manifest in various noticeable symptoms that affect the vehicle’s performance and drivability. Here are some common indicators drivers may experience when faced with a DPF clogged error:
1. Reduced Engine Power:
- Explanation: One of the most prevalent symptoms of a clogged DPF is a noticeable decrease in engine power. As the filter becomes obstructed with accumulated soot and particulate matter, it restricts the flow of exhaust gases, impeding the engine’s ability to generate power efficiently.
2. Increased Exhaust Smoke:
- Explanation: Another telltale sign of DPF clogging is an increase in visible exhaust smoke, often appearing darker or denser than usual. This occurs because the trapped soot within the clogged filter is not effectively burned off during the regeneration process, leading to higher emissions of particulate matter.
3. Illumination of Dashboard Warning Lights:
- Explanation: Modern vehicles are equipped with onboard diagnostics systems that monitor various components and systems for abnormalities. When the system detects a problem with the DPF, such as insufficient regeneration activity or excessive back pressure, it triggers the illumination of dashboard warning lights. Common indicators include the Check Engine Light (CEL) or the DPF warning light.
4. Poor Fuel Efficiency:
- Explanation: A clogged DPF can negatively impact fuel efficiency due to increased engine load and restricted exhaust flow. Drivers may notice a decrease in miles per gallon (MPG) as the engine struggles to operate efficiently under these conditions.
5. Limp Mode Activation:
- Explanation: In severe cases of DPF clogging, the vehicle’s onboard computer may activate a safety feature known as limp mode. This mode limits engine power and performance to prevent further damage to the engine or emissions system. Drivers may experience significantly reduced acceleration and overall drivability when limp mode is engaged.
6. Unusual Smells or Noises:
- Explanation: A clogged DPF can sometimes result in the emission of unusual smells or noises from the exhaust system. This may include a strong odor of unburned fuel or sulfur, as well as rattling or banging sounds caused by excessive back pressure within the exhaust system.
Recognizing the symptoms of a DPF clogged error is essential for proactive maintenance and timely intervention. Drivers should be vigilant for signs such as reduced engine power, increased exhaust smoke, dashboard warning light illumination, poor fuel efficiency, limp mode activation, and unusual smells or noises emanating from the vehicle’s exhaust system. Addressing DPF issues promptly can help prevent further damage to the engine and ensure optimal performance and emissions control.
Causes of DPF Clogging: Understanding the Culprits
The clogging of a Diesel Particulate Filter (DPF) can stem from a variety of factors, ranging from driving habits to external influences on the vehicle’s engine and emissions control system. Identifying these causes is crucial for mitigating the risk of DPF issues and maintaining optimal engine performance. Here are some common culprits behind DPF clogging:
1. Frequent Short Trips:
- Explanation: DPF regeneration, the process by which accumulated soot is burned off, typically occurs during sustained driving at higher speeds. Inadequate regeneration opportunities, such as frequent short trips or stop-and-go driving, can prevent the DPF from reaching the necessary temperature for effective regeneration, leading to soot buildup and eventual clogging.
2. Low-Quality Fuel:
- Explanation: Poor-quality diesel fuel may contain higher levels of contaminants, such as sulfur and particulate matter, which can accelerate the accumulation of soot in the DPF. Additionally, certain additives or impurities in low-quality fuel can interfere with the combustion process, resulting in increased emissions and soot production.
3. Engine Oil Contamination:
- Explanation: Contaminated engine oil, either due to improper maintenance or internal engine issues, can contribute to DPF clogging. Oil contaminants, such as unburned fuel or metal particles, can find their way into the exhaust system and deposit on the DPF, reducing its effectiveness over time.
4. Malfunctioning Emission Control Components:
- Explanation: Various components within the vehicle’s emission control system, such as the DPF pressure sensor, exhaust temperature sensor, or the selective catalytic reduction (SCR) system, play integral roles in monitoring and regulating emissions. Malfunctions or failures in these components can disrupt the DPF regeneration process, leading to inadequate soot removal and eventual clogging.
5. Inadequate Maintenance Practices:
- Explanation: Neglecting routine maintenance tasks, such as DPF inspections, engine oil changes, and emission system checks, can increase the likelihood of DPF clogging. Regular maintenance helps ensure that the DPF and related components remain clean and functioning optimally, reducing the risk of soot buildup and associated issues.
6. Environmental Factors:
- Explanation: Environmental factors, such as extreme temperatures, high humidity, or driving in dusty or polluted areas, can also impact DPF performance. Harsh operating conditions may hinder the effectiveness of DPF regeneration or accelerate soot accumulation, especially in vehicles subjected to frequent idling or heavy loads.
By addressing these underlying causes of DPF clogging and adopting proactive maintenance practices, drivers can minimize the risk of DPF-related issues and preserve the longevity of their vehicle’s engine and emissions control system. Regularly monitoring driving habits, fuel quality, engine oil condition, and emission control components can help identify potential issues early and prevent costly repairs down the road.
Diagnostic Procedures for P244B Error: Unraveling the Mystery
When faced with a P244B error code indicating a potential issue with the Diesel Particulate Filter (DPF) system, automotive technicians rely on a series of diagnostic procedures to pinpoint the root cause. Let’s explore the comprehensive approach technicians take to identify and resolve the underlying issue behind a P244B error:
1. Utilizing Diagnostic Scan Tools:
- Explanation: The first step in diagnosing a P244B error involves connecting a diagnostic scan tool to the vehicle’s onboard diagnostics (OBD) port. These tools allow technicians to retrieve fault codes stored in the vehicle’s electronic control unit (ECU) and perform system tests to assess the health of various components within the DPF system.
2. Retrieval of Fault Codes:
- Explanation: Diagnostic scan tools enable technicians to retrieve specific fault codes, such as P244B, that indicate problems within the DPF system. These codes provide valuable insight into the nature of the issue, allowing technicians to narrow down their diagnostic efforts and focus on relevant components and systems.
3. System Tests and Data Analysis:
- Explanation: After retrieving fault codes, technicians perform system tests using diagnostic scan tools to gather real-time data from sensors and components within the DPF system. This data includes parameters such as exhaust gas temperature, DPF pressure, and regeneration status, which help technicians identify abnormalities or discrepancies that may be contributing to the P244B error.
4. Inspection of DPF System and Components:
- Explanation: A crucial aspect of diagnosing a P244B error is conducting a thorough inspection of the DPF system and related components. Technicians visually inspect the DPF for signs of physical damage, excessive soot buildup, or blockages. Additionally, they check the integrity of components such as the DPF pressure sensor, exhaust temperature sensor, and diesel oxidation catalyst (DOC) for any malfunctions or failures that could trigger the error code.
5. Functional Tests and Regeneration Attempts:
- Explanation: Depending on the findings of initial system tests and inspections, technicians may perform functional tests to assess the responsiveness of DPF system components. This may involve initiating regeneration cycles using diagnostic scan tools to evaluate the effectiveness of soot removal and the overall functionality of the DPF system.
6. Collaboration and Expertise:
- Explanation: Diagnosing complex issues like a P244B error often requires collaboration among automotive technicians with specialized knowledge in diesel engine diagnostics and emissions control systems. By leveraging their expertise and experience, technicians can troubleshoot challenging issues more effectively and devise appropriate repair strategies.
Diagnosing a P244B error involves a systematic approach that combines the use of diagnostic scan tools, comprehensive system tests, thorough inspections of the DPF system, and collaboration among automotive professionals. By following these diagnostic procedures, technicians can accurately identify the root cause of the error and implement targeted repairs to restore the vehicle’s performance and emissions compliance.
Repair and Maintenance Solutions for DPF Clogged Error: Restoring Efficiency
When confronted with a DPF clogged error like P244B, prompt action is essential to restore the efficiency and functionality of the Diesel Particulate Filter (DPF) system. Here are several repair and maintenance solutions that automotive technicians may employ to address a DPF clogged error effectively:
1. Forced Regeneration:
- Description: One of the primary methods for clearing a clogged DPF is performing a forced regeneration. This process involves raising the exhaust gas temperature to facilitate the combustion of accumulated soot within the filter. Technicians use diagnostic scan tools to initiate a regeneration cycle and monitor the process to ensure proper soot removal.
2. Cleaning or Replacement of DPF:
- Description: In cases where a forced regeneration is ineffective or the DPF is severely clogged, technicians may opt to clean or replace the DPF altogether. Cleaning methods may include pneumatic or chemical cleaning processes to dislodge and remove stubborn soot deposits. If cleaning is not feasible, replacing the DPF with a new or refurbished unit may be necessary to restore optimal performance.
3. Repair or Replacement of Faulty Components:
- Description: Faulty sensors, valves, or other components within the DPF system can contribute to DPF clogging and trigger error codes like P244B. Technicians conduct diagnostic tests to identify and address any malfunctions or failures in these components. This may involve repairing damaged wiring, replacing defective sensors, or repairing/replacing malfunctioning valves to ensure proper DPF operation.
4. Emission Control System Maintenance:
- Description: Regular maintenance of the vehicle’s emission control system is essential for preventing DPF clogging and maintaining optimal performance. This includes routine inspections of the DPF and related components, such as sensors and valves, to detect any signs of wear or malfunction early. Additionally, adhering to recommended service intervals for engine oil changes, fuel filter replacements, and emissions system checks helps prevent issues that can contribute to DPF clogging.
5. Software Updates and Calibration:
- Description: In some cases, software updates or recalibration of the vehicle’s engine control module (ECM) may be necessary to address DPF-related issues. Manufacturers may release updates to improve DPF regeneration strategies, optimize engine performance, or address known issues that contribute to DPF clogging. Technicians can perform these updates using specialized diagnostic equipment to ensure compatibility and effectiveness.
6. Driver Education and Training:
- Description: Educating vehicle owners on proper driving habits and maintenance practices can help prevent DPF clogging and prolong the lifespan of the emission control system. Drivers should be encouraged to avoid frequent short trips, drive at consistent speeds to facilitate DPF regeneration, and use high-quality diesel fuel to minimize soot accumulation. Additionally, providing guidance on recognizing and responding to warning signs of DPF issues empowers drivers to take proactive measures to address potential problems early.
By implementing these repair and maintenance solutions, automotive technicians can effectively address a DPF clogged error like P244B and restore the performance and efficiency of the vehicle’s emission control system. Collaboration between technicians and vehicle owners is crucial for identifying and addressing underlying issues, ensuring optimal DPF operation, and reducing the risk of future problems.
Prevention Tips: Keeping Your DPF Healthy
Preventing DPF clogging and avoiding the occurrence of a P244B error code requires proactive measures and conscientious driving habits. Here are some practical tips for drivers to maintain a healthy Diesel Particulate Filter (DPF) system:
1. Drive at Highway Speeds Regularly:
- Tip: Make it a habit to take your vehicle for regular drives at highway speeds, especially if you primarily drive in urban or stop-and-go traffic conditions. Sustained highway driving allows the DPF to reach higher exhaust temperatures, facilitating more effective regeneration and preventing soot buildup.
2. Use High-Quality Fuel and Engine Oil:
- Tip: Opt for high-quality diesel fuel that meets or exceeds the specifications recommended by your vehicle manufacturer. Low-quality fuel may contain contaminants that accelerate soot accumulation in the DPF. Similarly, use engine oil that meets manufacturer specifications and adhere to recommended oil change intervals to minimize the risk of oil-related DPF issues.
3. Follow Manufacturer-Recommended Maintenance Schedules:
- Tip: Stay vigilant about following the manufacturer’s recommended maintenance schedules for your vehicle, including regular service intervals and DPF inspections. This ensures that the DPF and related components are kept in optimal condition and any potential issues are detected and addressed early.
4. Avoid Frequent Short Trips:
- Tip: Minimize the number of short trips whenever possible, as they may not provide sufficient opportunities for DPF regeneration. If short trips are unavoidable, consider combining errands into a single trip to allow the engine to reach operating temperatures and facilitate effective DPF regeneration.
5. Be Mindful of Driving Conditions:
- Tip: Be mindful of driving conditions that can impact DPF performance, such as heavy traffic, frequent idling, or towing heavy loads. These conditions can impede DPF regeneration and contribute to soot buildup. Whenever feasible, avoid prolonged idling and opt for routes with smoother traffic flow.
6. Pay Attention to Warning Signs:
- Tip: Familiarize yourself with the warning signs of potential DPF issues, such as reduced engine power, increased exhaust smoke, or illuminated dashboard warning lights. If you notice any abnormalities, such as the Check Engine Light (CEL) or the DPF warning light, address them promptly by consulting a qualified technician to prevent further damage.
7. Educate Yourself on DPF Maintenance:
- Tip: Take the time to educate yourself on proper DPF maintenance practices and guidelines provided by your vehicle manufacturer. Understanding how the DPF system works and what steps you can take to keep it functioning optimally empowers you to be proactive in preventing DPF-related issues.
By implementing these prevention tips and adopting responsible driving practices, you can minimize the risk of DPF clogging and reduce the likelihood of encountering a P244B error code. Remember that maintaining a healthy DPF system not only ensures optimal engine performance and fuel efficiency but also contributes to cleaner emissions and a healthier environment.
Conclusion: Understanding P244B and DPF Clogging
In this article, we’ve delved into the intricacies of the P244B error code and its implications for Diesel Particulate Filter (DPF) systems in diesel vehicles. Let’s recap the key points discussed and emphasize the significance of addressing DPF issues promptly:
1. Understanding P244B Error Code:
- We explored how the P244B error code serves as a diagnostic indicator of potential DPF clogging issues, highlighting the importance of proactive maintenance and prompt intervention.
2. Impact of DPF Clogging:
- DPF clogging can lead to various symptoms such as reduced engine power, increased exhaust smoke, and dashboard warning lights, adversely affecting vehicle performance and emissions compliance.
3. Diagnostic Procedures:
- Automotive technicians employ diagnostic scan tools and comprehensive inspection methods to identify the root cause of a P244B error, emphasizing the importance of collaboration and expertise in resolving complex DPF issues.
4. Repair and Maintenance Solutions:
- We discussed potential repair and maintenance solutions for addressing DPF clogging, including forced regeneration, DPF cleaning or replacement, and repair of faulty components within the emission control system.
5. Prevention Tips:
- Practical prevention tips were provided for drivers to minimize the risk of DPF clogging and avoid the occurrence of a P244B error code. These tips include driving at highway speeds regularly, using high-quality fuel and engine oil, and adhering to manufacturer-recommended maintenance schedules.
6. Importance of Prompt Action:
- Emphasized the importance of addressing DPF issues promptly to maintain the performance and longevity of diesel vehicles. Timely intervention not only preserves engine efficiency and fuel economy but also reduces the risk of costly repairs and ensures compliance with emissions regulations.
7. Encouragement for Drivers:
- Encouraged drivers to stay informed about their vehicle’s emission control system and seek professional assistance when necessary. Proactive maintenance and responsible driving habits play a crucial role in preserving the health of the DPF system and minimizing environmental impact.
In conclusion, maintaining a healthy DPF system is essential for diesel vehicle owners to ensure optimal performance, emissions compliance, and longevity. By staying informed, adopting preventive measures, and seeking timely assistance from qualified professionals, drivers can mitigate the risk of DPF-related issues and enjoy a smoother and more efficient driving experience.