Understanding and Addressing P2269: Water in Fuel – A Comprehensive Guide

Fault Code P2269 Water in Fuel Condition
Fault Code P2269, “Water in Fuel sensor faulty,” is a diagnostic trouble code (DTC) that indicates an issue related to the presence of water in the fuel system of a vehicle. This code typically triggers when the vehicle’s onboard computer detects a fault in the water in fuel sensor, which is responsible for monitoring the level of water present in the fuel.
Significance of Fuel Quality for Vehicle Performance
The quality of fuel plays a crucial role in determining the performance and longevity of a vehicle’s engine. Fuel contaminated with water or other impurities can lead to various problems, including reduced engine efficiency, decreased fuel economy, and potentially serious damage to engine components.
Importance of Addressing P2269 Promptly
It is essential to address Fault Code P2269 promptly to prevent potential damage to the vehicle’s engine and fuel system. Ignoring this issue can lead to further contamination of the fuel system, which may result in costly repairs and vehicle downtime. Additionally, prolonged exposure to water-contaminated fuel can cause corrosion and other damage to vital engine components, ultimately compromising the vehicle’s reliability and performance. Therefore, diagnosing and resolving P2269 in a timely manner is critical to maintaining the overall health and efficiency of the vehicle.

What is P2269: Water in Fuel?
Definition and Explanation of the P2269 Diagnostic Trouble Code
Fault Code P2269, “Water in Fuel sensor faulty,” is a specific diagnostic trouble code (DTC) that is stored in the vehicle’s onboard computer system when an issue related to water contamination in the fuel system is detected. The code typically indicates a malfunction or failure in the water in fuel sensor, which is responsible for monitoring the presence of water in the fuel.
When the water in fuel sensor detects an abnormal level of water in the fuel system, it triggers the P2269 code, alerting the vehicle’s operator to the potential problem. This allows for timely diagnosis and repair to prevent further damage to the engine and fuel system components.
Causes of Water Contamination in Fuel Systems
Water contamination in fuel systems can occur due to various reasons, including:
- Condensation: Moisture can accumulate in fuel tanks due to temperature fluctuations, leading to condensation and water buildup.
- Poor Fuel Quality: Low-quality or contaminated fuel may contain higher levels of water, which can enter the fuel system and cause issues.
- Leaks: Damaged fuel tanks or components in the fuel system can allow water to enter and contaminate the fuel.
- Improper Storage: Improper storage of fuel in open containers or exposed tanks can increase the risk of water contamination.
Identifying and addressing the root cause of water contamination is essential to prevent recurring issues and ensure the long-term reliability of the vehicle’s fuel system.
Impact of Water in Fuel on Engine Performance and Efficiency
Water contamination in the fuel system can have detrimental effects on engine performance and efficiency, including:
- Reduced Combustion Efficiency: Water does not combust like fuel, leading to incomplete combustion and decreased engine efficiency.
- Engine Misfires: Excessive water in the fuel mixture can cause misfires, resulting in rough idling, hesitation, and decreased power.
- Corrosion: Water can corrode fuel system components, such as fuel injectors, fuel lines, and the fuel pump, leading to costly repairs and potential safety hazards.
- Decreased Fuel Economy: Water contamination can disrupt the fuel-air ratio, leading to decreased fuel economy and increased fuel consumption.
- Engine Damage: Prolonged exposure to water-contaminated fuel can cause severe damage to engine components, resulting in engine failure and costly repairs.
Overall, addressing water contamination in the fuel system is crucial to maintaining optimal engine performance, fuel efficiency, and vehicle reliability. Regular inspection, proper maintenance, and prompt repair of any issues are essential steps in preventing water-related problems and ensuring the longevity of the vehicle’s fuel system.
Symptoms of P2269
A. Common Signs and Symptoms Indicating the Presence of Water in Fuel
Detecting water in fuel can be challenging, but there are several common signs and symptoms to watch for, including:
- Decreased Engine Performance: A noticeable decrease in engine power and responsiveness, especially during acceleration, can indicate water contamination in the fuel system.
- Rough Idling: The engine may idle roughly or inconsistently when water is present in the fuel, leading to unstable engine operation and vibrations.
- Stalling or Difficulty Starting: Water in the fuel can cause the engine to stall unexpectedly or experience difficulty starting, as the presence of water disrupts the combustion process.
- Engine Misfires: Water contamination can lead to engine misfires, resulting in sputtering or hesitation under load or during acceleration.
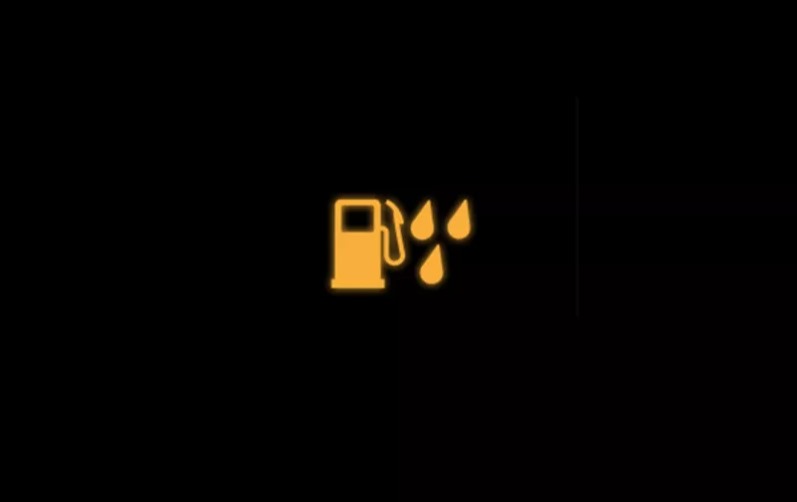
- Check Engine Light (CEL): The illumination of the check engine light on the vehicle’s dashboard is a common indication of a fault related to water in the fuel, often accompanied by the P2269 diagnostic trouble code.
- Unusual Engine Noises: Water in the fuel can cause knocking, pinging, or other unusual engine noises, indicating potential damage or irregular combustion.
B. How These Symptoms Manifest in Vehicle Performance
These symptoms can manifest in various ways, affecting the overall performance and drivability of the vehicle:
- Reduced Power and Efficiency: Water contamination disrupts the fuel-air mixture, leading to decreased engine power and fuel efficiency.
- Rough and Unstable Idling: The engine may idle erratically or stall due to irregular combustion caused by water in the fuel.
- Hesitation and Stalling: The presence of water can cause hesitation or stalling, particularly during acceleration or under load, as the engine struggles to maintain proper combustion.
- Increased Emissions: Water contamination can result in incomplete combustion, leading to higher emissions of pollutants such as carbon monoxide (CO) and hydrocarbons (HC).
- Potential Engine Damage: Ignoring the symptoms of water in fuel can lead to severe engine damage over time, including corrosion of fuel system components and internal engine damage.
C. Importance of Prompt Diagnosis and Repair
Prompt diagnosis and repair of water contamination in the fuel system are crucial to prevent further damage and maintain vehicle performance:
- Early detection allows for timely intervention to address the root cause of water contamination and prevent potential engine damage.
- Ignoring the symptoms of water in fuel can lead to costly repairs and downtime, as well as potential safety hazards on the road.
- Regular inspection and maintenance of the fuel system can help identify and address water contamination issues before they escalate, ensuring the long-term reliability and performance of the vehicle.
Recognizing the symptoms of water in fuel and taking prompt action to diagnose and repair the issue are essential steps in maintaining the overall health and efficiency of the vehicle’s fuel system, ultimately ensuring a smooth and reliable driving experience.
Diagnostic Process for P2269
Steps Involved in Diagnosing P2269
Diagnosing Fault Code P2269 involves a systematic approach to identify and address the underlying issue. The diagnostic process typically includes the following steps:
- Initial Inspection: Begin by visually inspecting the vehicle’s fuel system for any obvious signs of water contamination, such as moisture or corrosion around fuel system components.
- Retrieve Diagnostic Trouble Codes: Use a compatible diagnostic scan tool to retrieve the stored trouble codes from the vehicle’s onboard computer. Look specifically for the P2269 code related to the water in fuel sensor.
- Check for Other Codes: Check for any additional diagnostic trouble codes that may provide further insight into related issues or contributing factors.
- Inspect Water in Fuel Sensor: Perform a physical inspection of the water in fuel sensor and its wiring harness for any signs of damage, corrosion, or loose connections.
- Test Sensor Functionality: Use a multimeter or diagnostic tool to test the functionality of the water in fuel sensor. Verify that it is accurately detecting the presence of water in the fuel system.
- Inspect Fuel Quality: Test the quality of the fuel in the vehicle’s tank using a water detection kit or other appropriate testing methods. Check for the presence of water or other contaminants.
- Check Fuel System Components: Inspect other fuel system components, such as the fuel filter, fuel lines, and fuel injectors, for signs of water contamination or damage.
- Perform Functional Tests: Conduct functional tests on relevant components, such as the fuel pump and fuel pressure regulator, to ensure proper operation and identify any potential issues.
- Address Identified Issues: Based on the findings of the diagnostic process, repair or replace any faulty components, and address any underlying issues contributing to water contamination in the fuel system.
Introduction to Diagnostic Tools and Equipment Required
To diagnose Fault Code P2269 and identify water contamination in the fuel system, you will need the following diagnostic tools and equipment:
- Diagnostic Scan Tool: A compatible diagnostic scan tool is necessary to retrieve stored trouble codes from the vehicle’s onboard computer and perform diagnostic functions.
- Multimeter: A multimeter is useful for testing the functionality of electrical components, such as the water in fuel sensor, and verifying proper voltage and continuity.
- Water Detection Kit: A water detection kit allows you to test the quality of the fuel in the vehicle’s tank and detect the presence of water or other contaminants.
- Visual Inspection Tools: Basic tools for visual inspection, such as a flashlight and mirror, are essential for inspecting fuel system components for signs of damage or contamination.
- Safety Equipment: Personal protective equipment, including gloves and eye protection, should be worn when working with fuel and fuel system components to prevent injury.
Detailed Procedures for Identifying Water Contamination in the Fuel System
To identify water contamination in the fuel system, follow these detailed procedures:
- Visual Inspection: Inspect the exterior of the fuel tank and fuel lines for any signs of corrosion, rust, or moisture.
- Check Fuel Quality: Use a water detection kit to test a sample of the fuel from the vehicle’s tank for the presence of water. Follow the manufacturer’s instructions for proper testing procedures.
- Inspect Fuel Filter: Remove the fuel filter and inspect it for signs of water contamination or debris. Replace the fuel filter if necessary.
- Test Water in Fuel Sensor: Use a multimeter to test the functionality of the water in fuel sensor. Verify that it is sending the correct signals to the vehicle’s onboard computer.
- Check Fuel Pump: Test the fuel pump to ensure proper operation and pressure. A malfunctioning fuel pump can contribute to water contamination in the fuel system.
- Inspect Fuel Lines and Injectors: Inspect the fuel lines and injectors for any signs of water contamination, corrosion, or damage. Replace any damaged components as needed.
- Verify Repairs: After addressing any identified issues, retest the vehicle to ensure that the problem has been resolved and that no further issues are present.
By following these detailed procedures and utilizing the appropriate diagnostic tools and equipment, you can effectively identify water contamination in the fuel system and diagnose Fault Code P2269, ensuring proper repair and maintenance of the vehicle.
Addressing P2269: Water in Fuel
Prevention Methods to Minimize the Risk of Water Contamination
Preventing water contamination in the fuel system is key to avoiding issues such as Fault Code P2269. Here are some preventive measures:
- Use High-Quality Fuel: Always purchase fuel from reputable sources to minimize the risk of contamination.
- Regular Fuel System Maintenance: Maintain regular maintenance schedules for the fuel system, including fuel filter replacement and fuel tank inspections.
- Keep Fuel Tanks Full: Keeping fuel tanks full helps reduce condensation, minimizing the risk of water buildup in the tank.
- Proper Storage: Store fuel in sealed containers and keep them in a dry, cool environment to prevent water ingress.
- Water Separator Installation: Install a water separator in the fuel system to remove any water present before it reaches the engine.
Step-by-Step Guide for Repairing and Resolving P2269
Resolving Fault Code P2269 involves diagnosing and addressing the underlying issue. Here’s a step-by-step guide:
- Diagnostic Scan: Use a diagnostic scan tool to retrieve the trouble codes stored in the vehicle’s onboard computer, including P2269.
- Visual Inspection: Inspect the fuel system for any signs of water contamination, such as moisture or corrosion.
- Test Water in Fuel Sensor: Test the functionality of the water in fuel sensor using a multimeter or diagnostic tool.
- Check Fuel Quality: Test the quality of the fuel in the tank using a water detection kit to detect any water contamination.
- Inspect Fuel System Components: Inspect fuel system components, including the fuel filter, fuel lines, and injectors, for signs of water contamination or damage.
- Address Identified Issues: Repair or replace any faulty components contributing to water contamination in the fuel system.
- Clear Trouble Codes: After addressing the issues, clear the trouble codes stored in the vehicle’s onboard computer using the diagnostic scan tool.
- Test Drive: Test drive the vehicle to ensure that the problem has been resolved and that no further issues are present.
Importance of Professional Assistance and When to Seek It
While some DIY enthusiasts may be able to diagnose and repair simple issues, seeking professional assistance is often necessary for more complex problems. Here’s when to seek professional help:
- Lack of Experience: If you’re not experienced in diagnosing or repairing automotive issues, it’s best to seek assistance from a qualified mechanic.
- Complex Repairs: If the diagnostic process uncovers complex issues beyond your expertise, professional assistance may be required to ensure proper repair.
- Specialized Equipment: Some diagnostic tests require specialized equipment or tools that may not be available to DIYers.
- Warranty Concerns: If your vehicle is under warranty, it’s advisable to seek assistance from an authorized dealership or repair center to avoid voiding the warranty.
While DIY diagnosis and repair may be feasible for some, seeking professional assistance ensures that complex issues like P2269 are properly addressed, minimizing the risk of further damage and ensuring the long-term reliability of the vehicle.
Impact on Vehicle Performance and Longevity
Long-term Effects of Driving with Water-Contaminated Fuel
Driving with water-contaminated fuel can have severe long-term effects on vehicle performance and longevity. Some of the consequences include:
- Corrosion: Water in fuel can cause corrosion of critical engine components, including fuel injectors, fuel lines, and the fuel pump. Over time, corrosion weakens these parts, leading to leaks, malfunctions, and potential engine failure.
- Engine Damage: Water in fuel disrupts the combustion process, leading to incomplete combustion and increased wear on engine components. This can result in reduced engine performance, increased emissions, and ultimately, engine damage if left unresolved.
- Fuel System Degradation: Continuous exposure to water-contaminated fuel can degrade the entire fuel system, including the fuel tank, fuel lines, and fuel injectors. This degradation compromises the efficiency and reliability of the fuel system, leading to poor vehicle performance and increased maintenance costs.
- Fuel Efficiency Reduction: Water in fuel decreases the energy content of the fuel mixture, leading to reduced fuel efficiency and increased fuel consumption. This not only impacts the vehicle’s performance but also results in higher operating costs for the owner.
- Emission Increase: Incomplete combustion caused by water-contaminated fuel leads to higher emissions of harmful pollutants, such as carbon monoxide (CO) and hydrocarbons (HC). This contributes to environmental pollution and may result in regulatory compliance issues for the vehicle owner.
Potential Damage to Engine Components
Driving with water-contaminated fuel poses a significant risk of damage to various engine components, including:
- Fuel Injectors: Water can damage fuel injectors by causing corrosion and clogging. This results in poor fuel atomization, uneven fuel distribution, and ultimately, engine misfires and reduced performance.
- Fuel Pump: Water contamination can damage the fuel pump by causing corrosion or erosion of internal components. A damaged fuel pump may fail to deliver fuel at the required pressure, leading to engine stalling or failure to start.
- Cylinder Walls and Pistons: In severe cases, water in fuel can wash away the lubricating oil film on cylinder walls and piston rings, leading to increased friction and wear. This can result in piston scuffing, cylinder wall scoring, and ultimately, engine seizure.
- Valves and Valve Seats: Water-contaminated fuel can cause corrosion of valve components, leading to valve sticking or valve seat recession. This affects engine airflow and combustion efficiency, resulting in decreased power and increased emissions.
- Oxygen Sensors: Water in fuel can damage oxygen sensors by causing corrosion or contamination of sensor elements. A faulty oxygen sensor can lead to incorrect fuel mixture control, poor fuel economy, and increased emissions.
Importance of Regular Maintenance to Prevent P2269 and Similar Issues
Regular maintenance is essential for preventing issues like P2269 and minimizing the risk of water contamination in the fuel system. Some key maintenance practices include:
- Fuel System Inspections: Regularly inspect the fuel system for signs of leaks, corrosion, or contamination. Address any issues promptly to prevent water ingress into the fuel system.
- Fuel Filter Replacement: Replace the fuel filter at recommended intervals to ensure proper filtration of fuel and prevent water and contaminants from reaching the engine.
- Fuel Quality Monitoring: Use fuel from reputable sources and monitor fuel quality regularly using water detection kits or other testing methods. Avoid purchasing fuel from stations with poor storage practices or suspected contamination issues.
- Water Separator Installation: Consider installing a water separator in the fuel system to remove any water present before it reaches the engine. This helps prevent issues associated with water-contaminated fuel.
- Professional Inspections: Schedule regular inspections by a qualified mechanic to assess the overall condition of the fuel system and address any potential issues before they escalate.
By prioritizing regular maintenance and taking proactive measures to prevent water contamination in the fuel system, vehicle owners can safeguard their vehicles against issues like P2269 and ensure optimal performance and longevity in the long run.
Conclusion
Recap of Key Points Discussed in the Article
Throughout this article, we have covered various aspects related to Fault Code P2269: Water in Fuel. Here’s a recap of the key points discussed:
- Introduction to P2269: We introduced Fault Code P2269 and its significance as a diagnostic trouble code related to water contamination in the fuel system.
- Symptoms of P2269: We outlined common signs and symptoms indicating the presence of water in fuel, along with their potential impact on vehicle performance.
- Diagnostic Process: We provided an overview of the diagnostic process for P2269, including steps for identifying water contamination in the fuel system and the use of diagnostic tools and equipment.
- Addressing P2269: We discussed prevention methods, repair procedures, and the importance of seeking professional assistance to resolve P2269 and prevent future occurrences.
- Impact on Vehicle Performance and Longevity: We examined the long-term effects of driving with water-contaminated fuel and the potential damage to engine components.
Emphasis on the Significance of Clean Fuel and Proactive Maintenance
It’s evident that clean fuel and proactive maintenance are paramount to ensuring the optimal performance and longevity of a vehicle. By adhering to preventive measures such as using high-quality fuel, regularly inspecting the fuel system, and replacing fuel filters at recommended intervals, vehicle owners can minimize the risk of water contamination and associated issues like P2269. Additionally, the installation of water separators and professional inspections further enhances the resilience of the fuel system against potential contaminants.
Final Thoughts on the Importance of Addressing P2269 Promptly to Ensure Optimal Vehicle Performance and Longevity
In conclusion, addressing Fault Code P2269 promptly is crucial for maintaining optimal vehicle performance and longevity. Ignoring the symptoms of water contamination in the fuel system can lead to severe engine damage, increased emissions, and decreased fuel efficiency. By diagnosing and resolving P2269 in a timely manner, vehicle owners can mitigate the risk of further damage, ensure the reliability of their vehicles, and ultimately, prolong their lifespan. Clean fuel, proactive maintenance, and swift action in response to diagnostic trouble codes are essential practices for safeguarding the health and efficiency of the fuel system, thereby enhancing the overall driving experience and preserving the value of the vehicle for years to come.