Troubleshooting P24A2: Understanding Incomplete DPF Regeneration

Introduction – Understanding DPF Regeneration
DPF regeneration, or Diesel Particulate Filter regeneration, is a crucial process in modern diesel vehicles designed to reduce harmful emissions. The Diesel Particulate Filter (DPF) captures and stores exhaust soot particles to prevent them from being released into the atmosphere. Over time, these particles accumulate and can clog the filter, leading to decreased engine performance and increased emissions.
Introduction to P24A2 Fault Code
One common issue associated with DPF regeneration is the occurrence of fault codes, such as P24A2. This fault code specifically indicates that the regeneration process for the DPF was incomplete. Incomplete regeneration means that the accumulated soot particles have not been adequately burned off, resulting in a partially clogged filter.
Importance of Addressing Incomplete DPF Regeneration Promptly
Promptly addressing incomplete DPF regeneration is of utmost importance for several reasons:
- Preventing Engine Damage: Incomplete regeneration can lead to increased back pressure in the exhaust system, which can ultimately damage vital engine components such as turbochargers and EGR valves.
- Maintaining Fuel Efficiency: A partially clogged DPF can restrict exhaust flow, forcing the engine to work harder and consume more fuel to maintain performance. Addressing regeneration issues promptly helps in preserving fuel efficiency.
- Avoiding Costly Repairs: Ignoring incomplete regeneration can escalate into more severe issues over time, potentially necessitating costly repairs or even DPF replacement. By addressing the issue promptly, vehicle owners can avoid these expenses.
- Reducing Emissions: Proper DPF regeneration is essential for minimizing emissions of harmful pollutants into the environment. Addressing incomplete regeneration promptly ensures that the vehicle continues to meet emission standards and reduces its overall environmental impact.
In the subsequent sections, we will delve deeper into the causes of incomplete DPF regeneration and discuss effective strategies for resolving this issue to maintain optimal vehicle performance and environmental compliance.

Signs and Symptoms of Incomplete Regeneration
Incomplete regeneration of the Diesel Particulate Filter (DPF) can manifest through various signs and symptoms, indicating potential issues with the vehicle’s emission control system. Recognizing these signs promptly is crucial for addressing regeneration problems before they escalate into more severe issues. Here are the common indicators of incomplete regeneration:
1. Engine Warning Lights:
One of the most prominent signs of incomplete regeneration is the illumination of the engine warning light on the vehicle’s dashboard. When the onboard diagnostics system detects a fault related to the DPF regeneration process, it triggers the engine warning light to alert the driver of a potential issue. Common fault codes associated with incomplete regeneration include P24A2, indicating that regeneration was not completed successfully.
2. Decreased Performance and Fuel Efficiency
Incomplete regeneration can negatively impact the performance and fuel efficiency of the vehicle. As the DPF becomes clogged with soot particles, it restricts exhaust flow and hampers engine performance. Drivers may notice a decrease in acceleration, sluggishness, or a noticeable reduction in fuel efficiency. The engine may also struggle to maintain consistent power output, especially during acceleration or uphill driving.
3. Increased Exhaust Emissions:
A telltale sign of incomplete regeneration is an increase in exhaust emissions, particularly visible in vehicles equipped with diesel engines. Incomplete combustion of soot particles results in the release of unburned hydrocarbons and particulate matter into the atmosphere, leading to darker or denser exhaust smoke. Observing excessive smoke emission from the vehicle’s exhaust, especially during acceleration or idle, indicates a potential regeneration issue.
4. Diesel Smell or Smoke from the Exhaust:
In addition to increased exhaust emissions, incomplete regeneration may also produce noticeable odors or smoke from the vehicle’s exhaust. Drivers may detect a distinct diesel smell or observe black smoke emanating from the tailpipe, indicating inefficient combustion of diesel fuel and soot particles. These emissions not only contribute to air pollution but also signify an underlying problem with the DPF regeneration process.
Recognizing the signs and symptoms of incomplete regeneration is crucial for maintaining the performance, efficiency, and environmental compliance of diesel vehicles. If any of these indicators are observed, it is essential to address the issue promptly to prevent further damage to the DPF and ensure optimal vehicle operation. Consulting a qualified mechanic or technician is recommended for diagnosing and resolving regeneration issues effectively.
Diagnostic Process
Importance of Proper Diagnostic Tools
Effective diagnosis of DPF regeneration issues, including the P24A2 fault code, relies heavily on the use of proper diagnostic tools. Modern vehicles are equipped with sophisticated onboard diagnostics systems that monitor various engine parameters and emission control components. Specialized diagnostic scanners and software are essential for accessing these systems, retrieving fault codes, and conducting comprehensive diagnostics.
Steps for Diagnosing P24A2 Fault Code
- Initial Assessment: Begin by connecting a diagnostic scanner compatible with the vehicle’s onboard diagnostics system. Retrieve the stored fault codes to identify any issues related to DPF regeneration. The P24A2 fault code specifically indicates incomplete regeneration of the DPF.
- Examine Live Data: Access live data streams from relevant sensors and components to assess the condition of the DPF system during operation. Monitor parameters such as exhaust temperature, pressure differentials across the DPF, and oxygen sensor readings to identify abnormalities or irregularities that may hinder regeneration.
- Inspect DPF System Components: Physically inspect the DPF system components, including the DPF itself, sensors, and associated wiring harnesses, for signs of damage, corrosion, or contamination. Check for leaks or blockages in the exhaust system that could impede proper airflow or exhaust gas circulation.
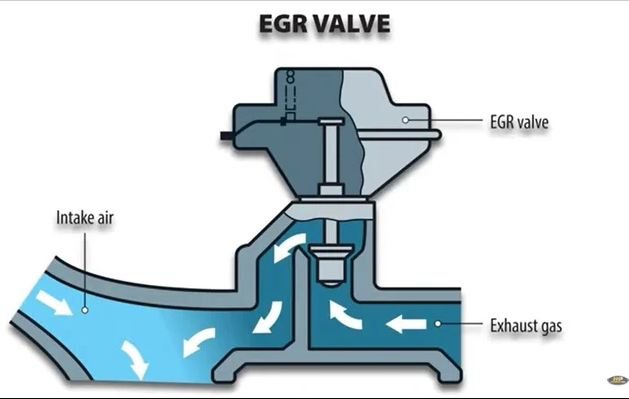
- Check EGR System: The Exhaust Gas Recirculation (EGR) system plays a crucial role in DPF regeneration by controlling exhaust gas flow and temperature. Inspect the EGR valve, cooler, and related components for proper operation and cleanliness. Malfunctioning EGR components can hinder regeneration and contribute to the occurrence of fault codes like P24A2.
- Test Regeneration Functionality: Conduct a manual or forced regeneration procedure using diagnostic software capable of initiating regeneration commands. Monitor the regeneration process closely for any errors or abnormalities, such as failure to reach target temperatures or incomplete regeneration cycles.
Common Related Issues to Consider
- Clogged DPF: A primary cause of incomplete regeneration is a clogged or saturated DPF, preventing proper exhaust gas flow and soot combustion. Insufficient driving conditions, fuel quality issues, or underlying engine problems can contribute to DPF clogging.
- Faulty Sensors: Malfunctioning sensors, such as exhaust gas temperature sensors or differential pressure sensors, can provide inaccurate data to the ECU, leading to improper DPF regeneration control. Inspect and test sensors for proper operation and replace any faulty components as necessary.
- EGR System Malfunction: Problems with the EGR system, including stuck valves, leaks, or carbon buildup, can disrupt exhaust gas recirculation and temperature control, affecting DPF regeneration performance. Verify the functionality of EGR components and address any issues identified during diagnosis.
- Engine Mechanical Issues: Underlying engine mechanical problems, such as worn piston rings, leaky injectors, or turbocharger issues, can indirectly impact DPF regeneration by affecting exhaust gas composition and temperature. Conduct a thorough inspection of engine components and address any mechanical issues discovered.
By following these steps and considering common related issues, technicians can effectively diagnose and resolve DPF regeneration problems, including the P24A2 fault code, ensuring optimal vehicle performance and emission compliance.
Possible Causes of P24A2
The P24A2 fault code, indicating incomplete DPF regeneration, can stem from various underlying issues within the vehicle’s emission control system. Identifying the root cause is essential for accurate diagnosis and effective resolution. Here are the possible causes associated with the P24A2 fault code:
1. Exhaust Gas Temperature Sensor Malfunction:
Malfunctioning exhaust gas temperature (EGT) sensors can provide inaccurate readings to the engine control unit (ECU), affecting its ability to monitor and control DPF regeneration. A faulty EGT sensor may fail to accurately detect exhaust temperature changes, leading to improper regeneration cycles and the occurrence of fault code P24A2.
2. Faulty DPF Pressure Sensor:
The DPF pressure sensor monitors the pressure differentials across the diesel particulate filter (DPF) to determine its level of saturation and the need for regeneration. A malfunctioning pressure sensor may provide incorrect data to the ECU, resulting in inadequate regeneration or premature triggering of regeneration cycles, leading to the P24A2 fault code.
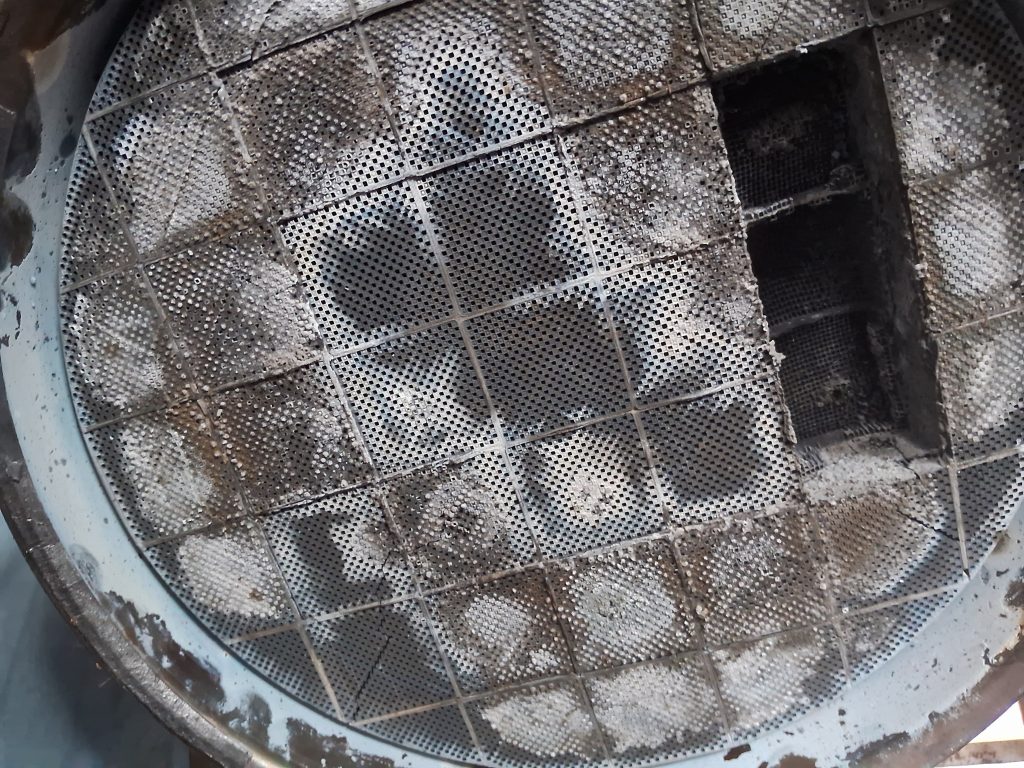
3. Clogged DPF or Exhaust System:
A primary cause of incomplete regeneration and the P24A2 fault code is a clogged or saturated DPF. Accumulated soot particles can obstruct the DPF’s porous structure, impeding exhaust gas flow and hindering regeneration. Additionally, blockages or restrictions in the exhaust system, such as damaged or collapsed pipes, can disrupt exhaust gas circulation and contribute to regeneration issues.
4. Software or Programming Issues:
Software glitches or programming errors within the engine control module (ECM) can interfere with the proper operation of the DPF regeneration system, leading to incomplete regeneration and the triggering of fault codes like P24A2. Issues such as outdated software, calibration discrepancies, or communication errors between vehicle modules may require reprogramming or software updates to rectify.
Addressing the P24A2 fault code effectively involves diagnosing and resolving the underlying cause(s) contributing to incomplete DPF regeneration. By inspecting and testing components such as EGT sensors, DPF pressure sensors, the DPF itself, and analyzing software parameters, technicians can pinpoint the specific issue and implement appropriate repairs or adjustments to restore proper DPF function and ensure emission compliance.
Troubleshooting Steps for P24A2 Fault Code
When confronted with the P24A2 fault code indicating incomplete DPF regeneration, a systematic approach to troubleshooting is essential for identifying and resolving underlying issues. Here are the recommended troubleshooting steps:
1. Checking Exhaust Gas Temperature Sensor:
Begin by inspecting the exhaust gas temperature (EGT) sensor(s) to ensure they are functioning correctly. Use diagnostic tools to monitor EGT sensor readings during engine operation and regeneration cycles. Verify that the sensors respond accurately to changes in exhaust temperature. Replace any faulty EGT sensors as necessary.
2. Testing DPF Pressure Sensor:
Test the diesel particulate filter (DPF) pressure sensor to verify its functionality. Use diagnostic equipment to measure pressure differentials across the DPF before and during regeneration cycles. Compare the sensor readings to manufacturer specifications. Replace the DPF pressure sensor if it fails to provide accurate data or exhibits irregularities. DPF Pressure Sensor is also called Delta-P Sensor
3. Inspecting DPF and Exhaust System for Blockages:
Physically inspect the DPF and exhaust system components for blockages or obstructions that may hinder exhaust gas flow. Remove the DPF and visually inspect its interior for excessive soot buildup or clogging. Check for damaged or collapsed exhaust pipes, mufflers, or catalytic converters that may restrict exhaust flow. Clear any blockages or replace damaged components as needed.
4. Updating Software or Reprogramming Control Modules:
Check for available software updates or reprogramming procedures provided by the vehicle manufacturer. Software glitches or programming errors within the engine control module (ECM) may contribute to regeneration issues and the occurrence of fault codes like P24A2. Perform software updates or reprogramming according to manufacturer recommendations to address any known issues and ensure optimal DPF regeneration performance.
By systematically following these troubleshooting steps, technicians can identify and address the underlying causes of the P24A2 fault code, restoring proper DPF function and ensuring emission compliance. If the issue persists or additional complications arise, consult manufacturer service manuals or seek assistance from qualified automotive professionals.
Preventive Measures for DPF Regeneration Issues
To minimize the occurrence of DPF regeneration issues, including the P24A2 fault code indicating incomplete regeneration, proactive preventive measures are essential. Implementing the following practices can help maintain optimal DPF function and prevent regeneration-related problems:
1. Regular Maintenance Schedules:
Adhere to manufacturer-recommended maintenance schedules for your vehicle, including routine inspections and servicing of emission control components. Regular maintenance helps identify and address potential issues before they escalate into more significant problems, ensuring the proper functioning of the DPF system.
2. Proper Driving Habits to Promote Regeneration:
Foster driving habits conducive to DPF regeneration, especially for vehicles primarily used for short trips or urban driving. Incorporate occasional long-distance journeys or highway driving sessions into your driving routine to promote passive regeneration of the DPF. Maintaining consistent speeds and avoiding frequent stop-and-go driving can help achieve optimal exhaust temperatures for effective regeneration.
3. Use of Quality Diesel Fuel:
Choose high-quality diesel fuel from reputable suppliers to minimize the risk of fuel-related issues affecting DPF performance. Quality diesel fuel contains fewer impurities and additives that can contribute to DPF clogging or contamination. Avoid using biodiesel blends or low-quality fuel sources that may leave behind deposits and accelerate DPF deterioration.
4. Regular DPF Inspection and Cleaning:
Periodically inspect the DPF for signs of soot buildup, clogging, or damage. Depending on vehicle usage and operating conditions, consider scheduling professional DPF cleaning services or performing manual regeneration procedures as part of preventive maintenance. Regular cleaning helps maintain DPF efficiency and prolong its service life, reducing the likelihood of regeneration-related issues.
5. Addressing Engine Performance Issues Promptly:
Address any engine performance issues, such as misfires, excessive exhaust smoke, or loss of power, promptly to prevent adverse effects on DPF regeneration. Engine malfunctions can contribute to increased soot accumulation and hinder regeneration effectiveness, leading to the occurrence of fault codes like P24A2.
By integrating these preventive measures into your vehicle maintenance and driving practices, you can mitigate the risk of DPF regeneration issues and ensure the long-term reliability and efficiency of your vehicle’s emission control system. Prioritize proactive care and attention to maintain optimal DPF function and minimize the need for costly repairs or component replacements.
When to Seek Professional Help:
If you encounter the P24A2 fault code or experience symptoms of incomplete DPF regeneration despite implementing preventive measures and troubleshooting steps, it may be time to seek professional assistance. Here are indicators that you should consult a qualified automotive technician:
- Persistent Fault Codes: If the P24A2 fault code persists after attempting troubleshooting steps, professional diagnostic tools and expertise may be necessary to identify and resolve the underlying issue.
- Unresolved Symptoms: Continued symptoms such as decreased performance, increased emissions, or unusual exhaust behavior despite preventive measures indicate a potential issue requiring professional attention.
- Complex Repairs: Repairing or replacing components such as sensors, the DPF, or engine-related systems may require specialized tools, knowledge, and skills best handled by trained professionals.
Importance of Addressing P24A2 Promptly:
Promptly addressing the P24A2 fault code and associated DPF regeneration issues is critical for several reasons:
- Prevention of Further Damage: Incomplete regeneration can lead to increased back pressure in the exhaust system, potentially causing damage to engine components and necessitating costly repairs.
- Preservation of Fuel Efficiency: Addressing regeneration issues promptly helps maintain optimal fuel efficiency by ensuring proper exhaust flow and engine performance.
- Emission Compliance: Proper DPF regeneration is essential for minimizing emissions of harmful pollutants into the environment. Prompt resolution of regeneration issues helps ensure compliance with emission standards and reduces environmental impact.
Conclusion:
The health and functionality of the Diesel Particulate Filter (DPF) play a crucial role in vehicle performance, fuel efficiency, and environmental sustainability. The occurrence of fault codes like P24A2 indicating incomplete DPF regeneration warrants immediate attention to prevent further complications and ensure optimal operation.
By adhering to regular maintenance schedules, promoting proper driving habits, and addressing issues promptly with professional assistance when needed, vehicle owners can maintain the health and efficiency of their DPF systems. Prioritizing DPF health not only enhances vehicle performance and longevity but also contributes to cleaner air and a healthier environment for all.
More Article Like This – https://faultscode.com/p2003-dpf-damaged-solutions/