Demystifying Fault Code P0420: Understanding Causes and Solutions
Brief Overview of Fault Code P0420
Fault Code P0420 is a diagnostic trouble code that specifically pertains to the efficiency of the catalytic converter in a vehicle’s exhaust system. This code is triggered when the On-Board Diagnostics (OBD) system detects that the catalytic converter is not performing within the expected parameters. As a result, it serves as an indication of potential issues within the vehicle’s emission control system.
Importance of Addressing P0420 Promptly
Addressing Fault Code P0420 promptly is crucial for maintaining the overall health and performance of your vehicle. Ignoring or delaying the resolution of this code can lead to more severe problems, including increased emissions, reduced fuel efficiency, and potential damage to other engine components. Timely intervention not only ensures compliance with emission standards but also prevents the escalation of issues that could result in more costly repairs down the line.
Significance of the Catalytic Converter in the Vehicle’s Exhaust System
Understanding the role of the catalytic converter is essential in comprehending the implications of Fault Code P0420. The catalytic converter plays a vital role in reducing harmful emissions by converting toxic gases produced during combustion into less harmful substances. Its efficiency directly impacts the environmental friendliness of your vehicle and ensures compliance with emission regulations. Therefore, any issues with the catalytic converter, as indicated by P0420, demand immediate attention to maintain optimal vehicle performance and environmental responsibility.

Understanding Fault Code P0420
Definition and Interpretation of P0420
Fault Code P0420 is a diagnostic trouble code that specifically indicates a potential issue with the efficiency of the catalytic converter in a vehicle’s exhaust system. When this code is triggered, it signifies that the catalytic converter is not operating at the expected efficiency levels, leading to increased emissions.
Diagnostic Process and How the Code is Triggered
The diagnostic process for Fault Code P0420 involves the vehicle’s On-Board Diagnostics (OBD) system monitoring the signals from the oxygen sensors. When the OBD system detects a significant decrease in the efficiency of the catalytic converter, it triggers the P0420 code. This process is crucial for identifying and addressing potential problems in the emission control system.
Common Misconceptions about P0420
There are several misconceptions surrounding P0420, with some assuming it is solely related to the catalytic converter’s complete failure. However, P0420 often indicates a decline in efficiency rather than an outright failure. Understanding this distinction is vital for accurate diagnosis and timely resolution.
Causes of Fault Code P0420
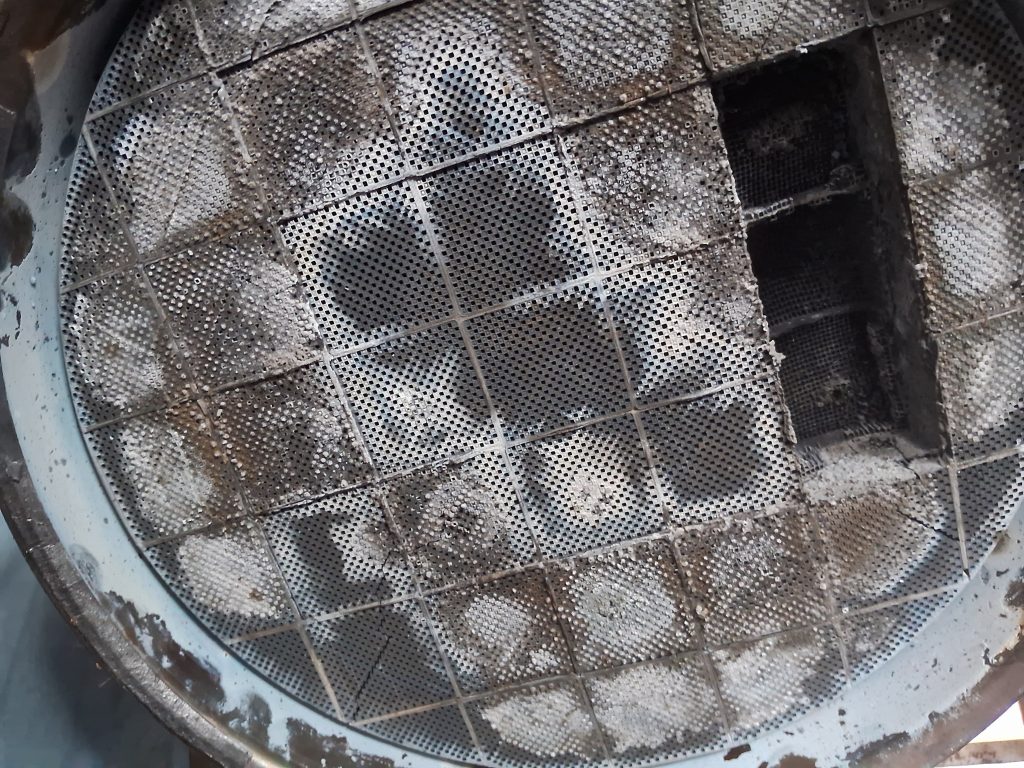
Faulty Catalytic Converter
- Wear and Tear Over Time The catalytic converter can degrade over time due to normal wear and tear. This deterioration may result from exposure to high temperatures and contaminants in the exhaust gases.
- Physical Damage or Impact Physical damage, such as dents or impacts, can compromise the integrity of the catalytic converter. Any structural damage may hinder its ability to function efficiently.
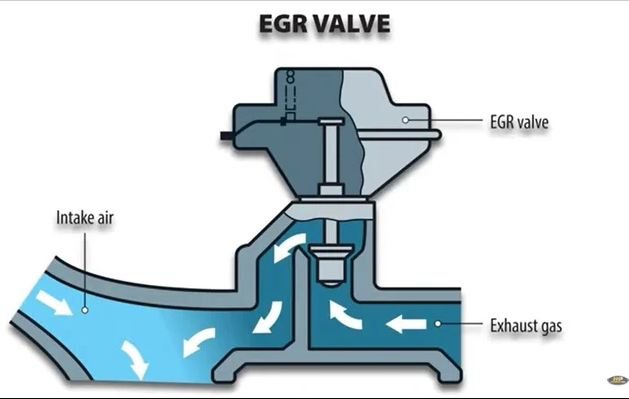
Oxygen Sensor Issues
- Malfunctioning Upstream Sensor (Bank 1) A malfunctioning upstream oxygen sensor can provide inaccurate data to the vehicle’s computer, leading to improper air-fuel mixture and, consequently, reduced catalytic converter efficiency.
- Malfunctioning Downstream Sensor (Bank 1) The downstream oxygen sensor monitors the efficiency of the catalytic converter. A malfunction in this sensor can result in inaccurate readings and trigger Fault Code P0420.
Exhaust System Leaks
- Identification and Impact on P0420 Exhaust system leaks, if left unaddressed, can contribute to the triggering of P0420. Identifying and fixing these leaks is crucial for maintaining proper exhaust system function.
- Common Locations of Leaks Exhaust leaks commonly occur at joints, connections, or due to corrosion. Regular inspection is necessary to detect and repair any leaks promptly.
Diagnostic Steps for Fault Code P0420
Using OBD-II Scanners for Diagnosis
Utilizing OBD-II scanners is the initial step in diagnosing Fault Code P0420. These scanners read and interpret the data from the vehicle’s On-Board Diagnostics system, providing detailed information about the specific issue triggering the code.
Visual Inspection of the Catalytic Converter
A visual inspection of the catalytic converter involves checking for physical damage, rust, or any signs of deterioration. Identifying these issues helps determine whether the catalytic converter requires further inspection or replacement.
Testing Oxygen Sensors
Testing the oxygen sensors, both upstream and downstream, is crucial. Proper functioning sensors ensure accurate data for the vehicle’s computer, contributing to optimal air-fuel mixture and catalytic converter efficiency.
Checking for Exhaust System Leaks
Exhaust system leaks can negatively impact catalytic converter efficiency. Thoroughly inspecting the exhaust system for leaks, using methods like a smoke test, can pinpoint the source of the problem.
Fixing Fault Code P0420
Catalytic Converter Replacement
- Options for Replacement When considering catalytic converter replacement, you have options such as OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer) or aftermarket converters. Choose a replacement that meets your vehicle’s specifications and emission standards.
- Tips for Choosing the Right Catalytic Converter Consider factors like material (ceramic or metallic substrate), vehicle compatibility, and warranty. Researching and consulting with professionals can help you make an informed decision.
Oxygen Sensor Replacement
- Importance of Using OEM Sensors Opt for OEM oxygen sensors to ensure compatibility and accurate readings. OEM sensors are specifically designed for your vehicle’s make and model, promoting seamless integration with the existing system.
- Proper Installation Procedures Follow manufacturer guidelines for proper sensor installation. Ensure correct placement and use the recommended tools to prevent damage during the installation process.
Repairing Exhaust System Leaks
- DIY vs. Professional Repair Small exhaust leaks may be repairable through do-it-yourself methods, such as using exhaust tape or sealant. However, significant leaks or those near the catalytic converter may require professional attention.
- Common Repair Methods Repair methods for exhaust leaks include welding, using clamps, or replacing damaged sections. Professional mechanics have the expertise to assess the extent of the damage and apply the most suitable repair method.
Preventive Measures
Regular Maintenance Practices to Prevent P0420
Incorporating regular maintenance practices can significantly reduce the risk of encountering Fault Code P0420. This includes routine inspections of the exhaust system, catalytic converter, and oxygen sensors. Scheduled maintenance, such as timely oil changes and using high-quality fuel, contributes to overall engine health, minimizing the likelihood of emission-related issues.
Importance of Timely Repairs for Related Issues
Timely repairs for issues related to the emission control system are paramount in preventing Fault Code P0420. Addressing minor problems promptly can prevent them from escalating into more severe issues that could compromise the efficiency of the catalytic converter. Regular vehicle check-ups and diagnostics play a crucial role in identifying and resolving potential concerns before they trigger P0420.
Monitoring Oxygen Sensor Performance
Regularly monitoring the performance of oxygen sensors is essential for preventing P0420. This can be done through OBD-II scans during routine maintenance or whenever the Check Engine Light illuminates. Promptly addressing any irregularities in oxygen sensor readings can help maintain the proper functioning of the catalytic converter and prevent the triggering of Fault Code P0420.
Conclusion – Fault Code P0420
Recap of Key Points
In summary, Fault Code P0420 serves as an indicator of potential issues with the catalytic converter’s efficiency. Understanding its causes, diagnostic steps, and preventive measures is crucial for maintaining the health and performance of your vehicle’s emission control system.
Emphasizing the Significance of Addressing P0420 Promptly
Addressing P0420 promptly is not just a matter of resolving a diagnostic trouble code; it is about ensuring the longevity and efficiency of your vehicle. Prompt intervention prevents a cascade of problems that could lead to increased emissions, decreased fuel efficiency, and more expensive repairs.
Encouraging Regular Vehicle Maintenance and Monitoring
In conclusion, regular vehicle maintenance, including inspections, diagnostics, and timely repairs, is the key to preventing Fault Code P0420 and ensuring the overall well-being of your vehicle. By staying proactive and addressing issues as they arise, you contribute to a cleaner environment, improved fuel efficiency, and a more reliable driving experience. Remember, a well-maintained vehicle not only benefits you but also the community and the environment as a whole.