Understanding and Resolving Fault Code P0118 – CTS Output Voltage Above Upper Limit

Introduction Fault Code P0118
Brief Overview of the Importance of the Coolant Temperature Sensor (CTS)
The Coolant Temperature Sensor (CTS) plays a pivotal role in the proper functioning of a vehicle’s engine. As a vital component of the engine management system, the CTS monitors the temperature of the engine coolant. This information is crucial for optimizing fuel injection, ignition timing, and various other engine functions. Understanding the significance of the CTS is essential for maintaining the overall health and performance of the vehicle.
Introduction to Fault Code P0118 and Its Significance
Fault Code P0118 is a diagnostic trouble code that specifically relates to the CTS. When this code is triggered, it indicates that the CTS output voltage is above the upper limit set by the manufacturer. This anomaly can have a significant impact on the engine’s performance and efficiency. In this article, we delve into the intricacies of P0118, exploring its implications and discussing the potential issues it may signify within the vehicle’s system.
Purpose of the Article: Understanding, Diagnosing, and Resolving P0118
The primary objective of this article is to provide a comprehensive guide for automotive enthusiasts, mechanics, and vehicle owners to understand, diagnose, and resolve Fault Code P0118. By unraveling the complexities of this diagnostic trouble code, readers will gain valuable insights into the inner workings of the CTS and its impact on the overall performance of the engine. Throughout the article, we will explore effective troubleshooting techniques and practical solutions to rectify the issues associated with P0118, ensuring optimal functionality of the Coolant Temperature Sensor and, consequently, the entire engine system.

Understanding the Coolant Temperature Sensor (CTS)
Explanation of the CTS Role in Engine Performance
The Coolant Temperature Sensor (CTS) is a critical component that actively contributes to the smooth functioning of a vehicle’s engine. Situated in the engine’s coolant system, the CTS is responsible for monitoring the temperature of the engine coolant. The data collected by the sensor is then transmitted to the Engine Control Module (ECM), influencing key engine parameters to ensure optimal performance.
Importance of Accurate Temperature Readings for the Engine Control Module (ECM)
Accurate temperature readings provided by the CTS are paramount for the Engine Control Module (ECM) to make real-time decisions that impact fuel injection, ignition timing, and other critical engine functions. The ECM relies on precise temperature information to calibrate the air-fuel mixture, preventing issues such as overheating, poor fuel efficiency, and increased emissions. Understanding the significance of these readings sheds light on the pivotal role the CTS plays in maintaining an efficient and well-balanced engine operation.
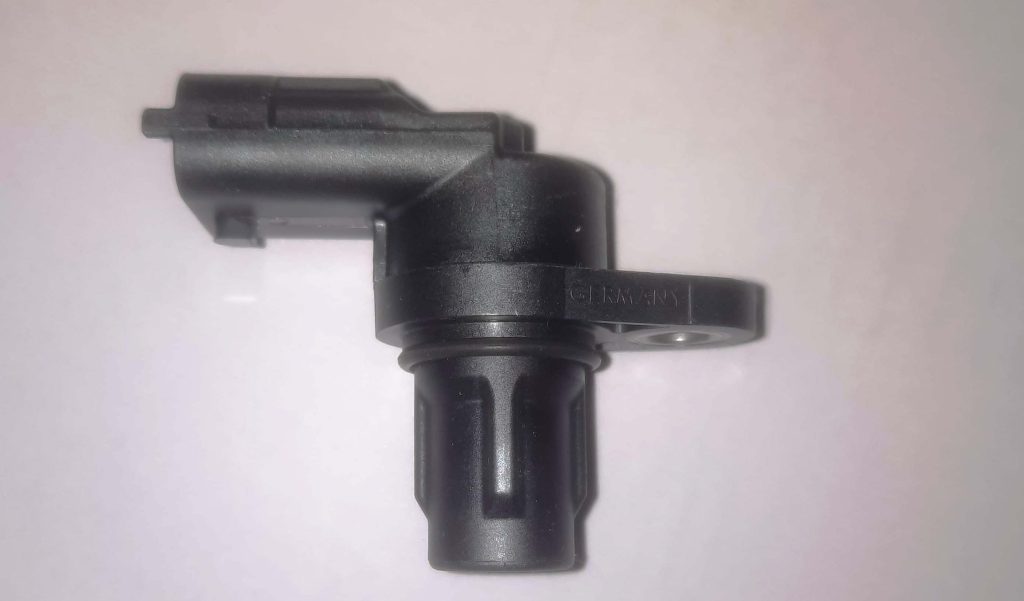
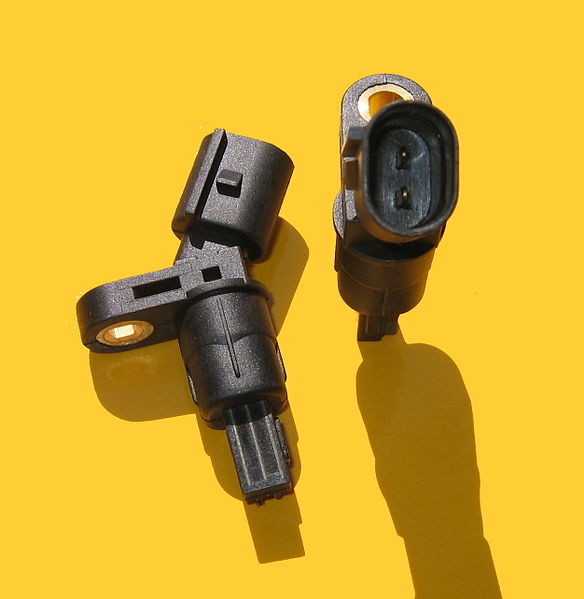
Overview of the CTS Components and Functionality
The Coolant Temperature Sensor is typically a thermistor, a type of resistor whose electrical resistance is dependent on temperature. As the engine temperature changes, the resistance of the CTS also varies. This dynamic resistance is then converted into an electrical voltage signal, which is sent to the ECM. Exploring the internal components and functionality of the CTS provides a deeper understanding of how this sensor translates temperature changes into actionable data for the ECM. This knowledge is essential for grasping the intricacies of Fault Code P0118 and its impact on the CTS.
Fault Code P0118: Causes and Symptoms
A. Definition of Fault Code P0118
Fault Code P0118 is a diagnostic trouble code that specifically points to an issue with the Coolant Temperature Sensor (CTS). When this code is triggered, it signifies that the CTS output voltage is registering above the upper limit prescribed by the vehicle manufacturer. This deviation from the expected range can lead to a range of issues affecting engine performance and overall vehicle efficiency.
B. Common Causes Leading to P0118 Activation
1. Faulty CTS
One of the primary culprits behind the activation of P0118 is a malfunctioning Coolant Temperature Sensor. Over time, these sensors can wear out or become inaccurate, providing erroneous temperature readings to the ECM.
2. Wiring Issues
Faulty or damaged wiring connected to the CTS can disrupt the proper transmission of signals to the ECM. Corrosion, frayed wires, or poor connections can lead to irregular voltage readings, triggering Fault Code P0118.
3. ECM Malfunctions
In some cases, the Engine Control Module (ECM) itself may be experiencing malfunctions. If the ECM is unable to accurately interpret the signals from the CTS, it can result in the activation of P0118.
C. Symptoms Associated with P0118
1. Engine Overheating
An inaccurate reading from the Coolant Temperature Sensor can lead to improper engine cooling. This can result in engine overheating, potentially causing severe damage to engine components.
2. Poor Fuel Efficiency
Fault Code P0118 can impact the air-fuel mixture, leading to suboptimal combustion. This can result in decreased fuel efficiency, meaning the vehicle covers fewer miles per gallon of fuel.
3. Illumination of the Check Engine Light
The activation of Fault Code P0118 typically prompts the illumination of the check engine light on the vehicle’s dashboard. This serves as an early warning system, indicating that there’s a problem with the CTS that requires attention.
Understanding these causes and symptoms is crucial for diagnosing and addressing Fault Code P0118 effectively. In the following sections, we’ll delve into the diagnostic process and explore potential solutions to rectify these issues.
Diagnosing Fault Code P0118
A. Preliminary Steps
1. Retrieving the Fault Code
The initial step in diagnosing Fault Code P0118 involves retrieving the code using an OBD-II scanner. This device connects to the vehicle’s onboard computer and provides specific trouble codes. P0118, once identified, serves as the starting point for further investigation.
2. Visual Inspection of the CTS and Related Components
Perform a thorough visual inspection of the Coolant Temperature Sensor (CTS) and its associated wiring. Look for signs of damage, corrosion, or loose connections. Addressing visible issues can often resolve problems triggering P0118.
B. Using a Multimeter for Voltage Testing
1. CTS Voltage Specifications
Refer to the vehicle’s service manual to determine the correct voltage specifications for the Coolant Temperature Sensor. This information is crucial for accurate diagnosis. Typically, CTS voltage should fall within a specified range, and deviations may trigger Fault Code P0118.
2. Step-by-Step Guide to Voltage Testing
- Ensure the vehicle is turned off and the key is removed.
- Disconnect the electrical connector from the CTS.
- Set the multimeter to the voltage setting.
- Connect the multimeter probes to the CTS terminals.
- Turn the ignition key to the “on” position without starting the engine.
- Compare the measured voltage with the specified range. A reading above the upper limit may indicate a faulty CTS.
C. Additional Diagnostic Tools and Techniques
1. OBD-II Scanner Data Analysis
Use an OBD-II scanner for in-depth data analysis beyond fault code retrieval. Monitor live data related to the CTS, such as coolant temperature readings. Anomalies in real-time data can provide valuable insights into the root cause of P0118.
2. Using a Scan Tool for Live Data Monitoring
Advanced scan tools with live data monitoring capabilities allow real-time observation of various engine parameters. Focus on CTS data, including temperature readings and voltage values. This dynamic analysis aids in identifying intermittent issues that may not be apparent during static testing.
By systematically applying these diagnostic steps and tools, you can pinpoint the cause of Fault Code P0118, whether it’s a malfunctioning CTS, wiring problem, or ECM issue. Once identified, appropriate corrective measures can be taken to address the underlying issue and restore the proper functioning of the Coolant Temperature Sensor.
Resolving Fault Code P0118
Repairing or Replacing the Coolant Temperature Sensor
1. Step-by-Step Sensor Replacement Guide
- Disconnect the Battery: Ensure the vehicle’s battery is disconnected to prevent electrical accidents.
- Locate the CTS: Identify the Coolant Temperature Sensor’s location, often on the engine or in the coolant system.
- Remove the Old Sensor: Carefully disconnect the electrical connector and remove the faulty CTS.
- Install the New Sensor: Place the new sensor in the same position, ensuring a secure fit.
- Reconnect the Electrical Connector: Securely reconnect the electrical connector to the new CTS.
- Reconnect the Battery: Reconnect the vehicle’s battery.
2. Calibration Procedures, If Applicable
Refer to the manufacturer’s specifications for any calibration procedures required after sensor replacement. Some vehicles may necessitate recalibration to ensure accurate temperature readings.
Addressing Wiring Issues
1. Identifying and Repairing Damaged Wiring
- Visual Inspection: Inspect the wiring connected to the CTS for visible damage, corrosion, or wear.
- Multimeter Testing: Use a multimeter to check for continuity and proper resistance along the wiring.
- Repair or Replace: Address any identified issues by repairing or replacing damaged wiring.
2. Ensuring Proper Electrical Connections
- Secure Connections: Ensure that all electrical connections, including those of the CTS, are securely fastened.
- Cleaning Contacts: Clean electrical contacts to remove any corrosion or debris that may hinder proper conductivity.
ECM Troubleshooting and Reprogramming
1. Overview of Potential ECM Malfunctions
- Diagnostic Tools: Use diagnostic tools, including OBD-II scanners, to identify potential malfunctions in the Engine Control Module (ECM).
- Visual Inspection: Check for visible signs of damage or overheating on the ECM.
2. Steps for Reprogramming the ECM, If Necessary
- Consult Manufacturer Guidelines: Refer to the vehicle manufacturer’s guidelines for ECM reprogramming procedures.
- Use Compatible Software: Utilize compatible software and tools for ECM reprogramming.
- Follow Step-by-Step Instructions: Adhere to step-by-step instructions provided by the manufacturer for successful ECM reprogramming.
By systematically addressing the root causes of Fault Code P0118, including CTS replacement, resolving wiring issues, and troubleshooting the ECM, you can effectively eliminate the trigger factors. Following these detailed steps ensures a comprehensive approach to resolving P0118 and restoring the optimal functioning of the Coolant Temperature Sensor within the engine management system.
Preventive Measures and Tips
A. Regular Maintenance to Avoid CTS Issues
1. Routine CTS Inspection
Incorporate regular inspections of the Coolant Temperature Sensor (CTS) into your vehicle maintenance routine. Check for signs of wear, corrosion, or damage during scheduled service intervals.
2. Scheduled Replacements
Consider replacing the CTS at manufacturer-recommended intervals, even if no issues are apparent. Preventive replacement helps maintain accurate temperature readings and reduces the risk of Fault Code P0118.
B. Monitoring Coolant Levels and System Health
1. Regular Coolant Checks
Frequently monitor coolant levels to ensure they are within the recommended range. Low coolant levels can affect the CTS’s accuracy and trigger fault codes.
2. Cooling System Maintenance
Maintain the overall health of the cooling system by flushing and replacing coolant as per the manufacturer’s guidelines. A well-functioning cooling system contributes to accurate temperature readings by the CTS.
C. Importance of Prompt Action When the Check Engine Light Illuminates
1. Immediate Inspection
When the check engine light illuminates, promptly perform a diagnostic scan to retrieve trouble codes. Delaying inspection and resolution may lead to further complications.
2. Professional Diagnosis
Seek professional assistance if you’re unable to identify or resolve the issue independently. Certified mechanics can perform in-depth diagnostics to pinpoint the cause of fault codes like P0118.
3. Timely Repairs
Address identified issues promptly to prevent potential damage to engine components and ensure the continued reliability of the vehicle. Timely repairs contribute to prolonged vehicle lifespan and performance.
Conclusion
A. Recap of Key Points
In conclusion, our exploration of Fault Code P0118 and the associated Coolant Temperature Sensor (CTS) has unveiled crucial insights into maintaining a healthy engine management system. Let’s recap the key points discussed in this comprehensive guide:
- The CTS plays a pivotal role in engine performance by monitoring engine coolant temperature.
- Fault Code P0118 is triggered when the CTS output voltage surpasses the upper limit set by the manufacturer.
- Causes of P0118 include a faulty CTS, wiring issues, and potential ECM malfunctions.
- Symptoms of P0118 encompass engine overheating, poor fuel efficiency, and the illumination of the check engine light.
B. Emphasis on the Significance of Addressing P0118 Promptly
Addressing Fault Code P0118 promptly is paramount to maintaining optimal engine performance and preventing potential damage. Ignoring the warning signs associated with P0118 can lead to severe consequences such as engine overheating, reduced fuel efficiency, and increased emissions. Timely diagnosis and resolution of P0118 ensure the longevity and reliability of the vehicle.
C. Encouragement for Regular Vehicle Maintenance and Diagnostics
As a proactive measure, regular vehicle maintenance and diagnostics are strongly encouraged. Incorporating routine inspections of the CTS, monitoring coolant levels, and promptly addressing check engine light warnings contribute to the overall health of the engine. Preventive measures, such as scheduled CTS replacements and cooling system maintenance, go a long way in avoiding issues like P0118.
In conclusion, a well-maintained vehicle is not only more reliable but also more fuel-efficient and environmentally friendly. By staying vigilant and taking proactive steps, vehicle owners can enjoy a smoother driving experience while ensuring the longevity and efficiency of their automobiles. Remember, a small investment in preventive maintenance can save you from costly repairs and unexpected breakdowns in the long run.
Understanding and Addressing P0563 High Battery Voltage: An In-depth Guide
: Understanding and Resolving Fault Code P0118 – CTS Output Voltage Above Upper Limit