Troubleshooting P0420: Best Diagnosing and Fixing the Issue

Fault codes in vehicles play a crucial role in diagnosing and resolving issues that may arise in the engine or other essential components. These codes act as indicators, helping both mechanics and vehicle owners identify problems swiftly and efficiently. In this article, we will delve into the significance of addressing fault codes promptly, with a specific focus on one common issue – Fault Code P0420.
Brief Explanation of Fault Codes in Vehicles
Fault codes, also known as Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs), are alphanumeric codes generated by a vehicle’s onboard diagnostics system (OBD-II). These codes provide insights into potential issues affecting the vehicle’s performance. Mechanics use specialized scanners to retrieve these codes, aiding in the diagnostic process.
Understanding these fault codes is essential for maintaining a vehicle’s health. They cover a wide range of issues, from engine malfunctions to problems with emission control systems. Promptly addressing fault codes ensures that any underlying problems are resolved before they escalate, preventing potential damage and reducing repair costs in the long run.
Importance of Addressing Fault Codes Promptly
Timely response to fault codes is crucial for several reasons. Firstly, it helps prevent minor issues from evolving into major problems, saving both time and money. Secondly, addressing fault codes promptly contributes to overall vehicle safety and performance, ensuring a smooth driving experience. Neglecting fault codes may lead to decreased fuel efficiency, increased emissions, and potential damage to other components.
Additionally, modern vehicles often have complex computerized systems that interconnect various parts. Ignoring fault codes may disrupt this intricate network, affecting the overall functionality of the vehicle. Regular maintenance and quick resolution of fault codes contribute to the longevity of the vehicle and enhance its overall reliability.
Introduction to Fault Code P0420 as a Common Issue
One prevalent fault code that vehicle owners encounter is P0420. This code is related to the vehicle’s catalytic converter, an integral component of the exhaust system. The catalytic converter plays a vital role in reducing harmful emissions by converting pollutants into less harmful substances. When the OBD-II system detects inefficiencies or malfunctions in the catalytic converter, it triggers the P0420 code.
In the following sections, we will explore the specifics of Fault Code P0420, its potential causes, and the necessary steps to address and rectify this common issue. Understanding P0420 is crucial for maintaining a vehicle’s environmental friendliness and ensuring compliance with emission standards.
What is Fault Code P0420?

Definition and Explanation of Fault Code P0420
Fault Code P0420 is a specific Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) that indicates a potential issue with the catalytic converter in a vehicle’s exhaust system. The catalytic converter is responsible for reducing harmful emissions by converting pollutants, such as carbon monoxide and nitrogen oxides, into less harmful substances like carbon dioxide and water. When the OBD-II system detects inefficiencies or malfunctions in the catalytic converter’s performance, it triggers the P0420 code.
How the OBD-II System Works to Detect Issues
The Onboard Diagnostics-II (OBD-II) system is a sophisticated system in modern vehicles that monitors and manages the vehicle’s performance. It utilizes a network of sensors strategically placed throughout the vehicle to gather data on various components, including the engine, exhaust, and transmission. These sensors continuously send information to the OBD-II system, which analyzes the data and identifies deviations from normal operating conditions.
When the system detects abnormalities, it generates specific fault codes, such as P0420, to alert the vehicle owner or mechanic to potential issues. These codes serve as a roadmap for diagnosing and addressing problems efficiently.
Importance of the Catalytic Converter in the Exhaust System
The catalytic converter is a critical component in the vehicle’s exhaust system. It plays a key role in reducing air pollution by converting harmful gases produced during combustion into less harmful substances. This process involves a catalyst that facilitates chemical reactions, transforming pollutants into water vapor, carbon dioxide, and nitrogen gas.
A properly functioning catalytic converter is essential for meeting environmental standards and ensuring that vehicles contribute to cleaner air quality. When the catalytic converter malfunctions, it not only triggers the P0420 code but also compromises the vehicle’s emission control capabilities.
Overview of the P0420 Code’s Significance
Fault Code P0420 holds significance as it directly points to potential issues with the catalytic converter. Ignoring or delaying the resolution of this code may lead to increased emissions, decreased fuel efficiency, and potential damage to other components. Additionally, addressing P0420 promptly is crucial for ensuring compliance with emission standards and maintaining a vehicle’s environmental friendliness.
In the subsequent sections, we will explore the common causes of P0420, methods for diagnosing the issue, and effective strategies for resolving the code to restore the catalytic converter’s optimal functionality. Understanding the intricacies of P0420 empowers vehicle owners to take proactive measures in addressing this common and impactful fault code.
Common Causes of Fault Code P0420
Aging or Failing Catalytic Converter
One of the primary culprits behind Fault Code P0420 is an aging or failing catalytic converter. Over time, the internal components of the catalytic converter may deteriorate, reducing its efficiency in converting harmful gases. This degradation can trigger the P0420 code as the OBD-II system recognizes a decline in the converter’s ability to meet emission standards.
Regular maintenance and timely replacement of a worn-out catalytic converter are crucial to prevent the recurrence of P0420 and ensure the vehicle’s compliance with environmental regulations.
Oxygen Sensor Malfunctions
Oxygen sensors play a pivotal role in monitoring the oxygen levels in the exhaust gases. Malfunctions in the oxygen sensors can lead to inaccurate readings, causing the OBD-II system to misinterpret the catalytic converter’s performance. This, in turn, can trigger Fault Code P0420.
Routine inspection and replacement of faulty oxygen sensors are essential for maintaining accurate data transmission to the OBD-II system and preventing false triggers of P0420.
Engine Misfires and Their Impact on Emissions
Engine misfires can significantly impact the emission levels of a vehicle. When the engine misfires, unburned fuel may reach the catalytic converter, causing overheating and potential damage. This condition can lead to the triggering of P0420, indicating a compromised catalytic converter.
Regular engine maintenance, including spark plug replacement and addressing misfires promptly, is crucial in preventing the occurrence of Fault Code P0420 due to engine-related issues.
Exhaust System Leaks and Their Role in Triggering the Code
Leaks in the exhaust system can introduce excess oxygen into the exhaust gases, disrupting the proper functioning of the catalytic converter. The OBD-II system may interpret this anomaly as a sign of converter inefficiency, triggering P0420.
Thorough inspection of the exhaust system, including the manifold and pipes, is essential to identify and repair any leaks promptly, preventing the recurrence of Fault Code P0420.
Fuel System Issues Leading to an Incorrect Air-Fuel Mixture
An incorrect air-fuel mixture can impact the combustion process and increase emissions. Issues such as a faulty fuel injector or a malfunctioning mass air flow sensor can disrupt the balance of the air-fuel mixture, potentially triggering P0420.
Regular inspection of the fuel system components and addressing any issues promptly can help maintain the proper air-fuel ratio, preventing the occurrence of Fault Code P0420 associated with fuel system-related problems.
Understanding these common causes of Fault Code P0420 is crucial for vehicle owners and mechanics alike. In the next sections, we will explore diagnostic methods and effective strategies for resolving P0420, ensuring the optimal performance of the catalytic converter and compliance with emission standards.
Diagnostic Steps for DTC P0420 Code
Using an OBD-II Scanner for Code Retrieval
The initial step in diagnosing Fault Code P0420 is to use an OBD-II scanner to retrieve the code. Connect the scanner to the vehicle’s OBD-II port, usually located beneath the dashboard. Retrieve and document the specific details of the P0420 code, including the freeze frame data, to provide insights into the conditions under which the code was triggered.
Interpreting Freeze Frame Data to Identify the Conditions Triggering the Code
Freeze frame data captured by the OBD-II system at the time of the P0420 code occurrence is valuable for pinpointing the conditions leading to the fault. Analyze the freeze frame data, including engine temperature, vehicle speed, and other relevant parameters. This information aids in understanding the circumstances triggering the code and guides the diagnostic process.
Performing a Visual Inspection of the Exhaust System Components
Conduct a thorough visual inspection of the exhaust system components to identify any visible issues. Check for physical damage, corrosion, or rust on the catalytic converter, exhaust pipes, and manifold. Additionally, inspect the connections and mounting brackets for signs of wear or looseness. Identifying and addressing visible concerns can contribute to the effective resolution of Fault Code P0420.
Testing Oxygen Sensors for Proper Functioning
Faulty oxygen sensors can contribute to the triggering of P0420. Use a multimeter or an oscilloscope to test the oxygen sensors for proper functioning. Measure the voltage output of the sensors, ensuring they respond appropriately to changes in the air-fuel mixture. Replace any malfunctioning sensors to restore accurate data transmission to the OBD-II system and mitigate the risk of recurring P0420.
Checking for Exhaust Leaks and Addressing Misfires
Exhaust leaks and engine misfires can impact the performance of the catalytic converter. Inspect the exhaust system for leaks, paying close attention to the manifold and exhaust pipes. Address any identified leaks promptly to prevent excess oxygen intake by the catalytic converter. Additionally, diagnose and resolve engine misfires, ensuring a balanced air-fuel mixture and preventing the recurrence of P0420.
Following these diagnostic steps systematically allows for a comprehensive evaluation of the potential causes behind Fault Code P0420. Once the specific issue or combination of issues contributing to the code is identified, appropriate corrective measures can be taken to restore the optimal functionality of the catalytic converter and address the root cause of the fault. In the subsequent sections, we will explore effective strategies for resolving P0420 and ensuring the long-term health of the vehicle’s emission control system.
Advanced Diagnostics and Testing
Utilizing Specialized Diagnostic Tools for a More In-depth Analysis
For a more comprehensive analysis of Fault Code P0420, consider utilizing specialized diagnostic tools beyond a standard OBD-II scanner. Advanced tools, such as emission analyzers and oscilloscopes, can provide detailed insights into the performance of various components. These tools allow for a more in-depth examination of sensor outputs, exhaust gas composition, and other critical parameters, aiding in the identification of subtle issues that may contribute to P0420.
Conducting a Catalytic Converter Efficiency Test
Performing a catalytic converter efficiency test is crucial to assess its performance accurately. Specialized testing equipment can measure the converter’s ability to reduce harmful emissions effectively. A decrease in efficiency may indicate internal degradation, supporting the diagnosis of Fault Code P0420. If the efficiency falls below acceptable levels, replacing the catalytic converter may be necessary to resolve the code and restore optimal emission control.
Verifying the Functionality of the Air-Fuel Ratio Sensors
In addition to standard oxygen sensors, modern vehicles often incorporate air-fuel ratio sensors. These sensors play a vital role in maintaining the optimal mixture for combustion. Utilize diagnostic tools to verify the functionality of air-fuel ratio sensors, ensuring they provide accurate readings. A malfunctioning sensor can contribute to an incorrect air-fuel mixture, potentially triggering P0420. Replacement of faulty sensors may be required for effective resolution.
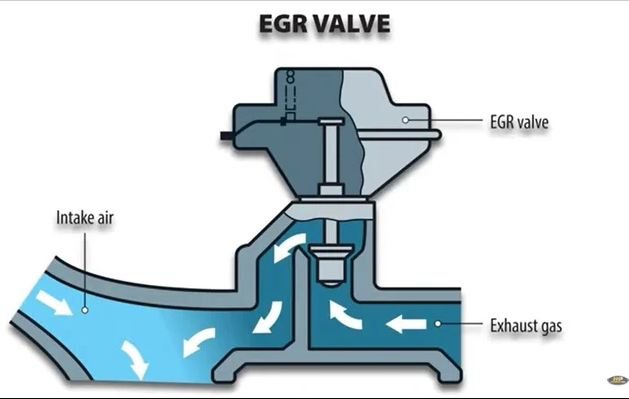
Inspecting the EGR System for Potential Issues
Exhaust Gas Recirculation (EGR) systems are designed to reduce nitrogen oxide emissions by recirculating a portion of exhaust gases back into the combustion process. Inspect the EGR system for potential issues, such as clogs or malfunctions, that may affect its operation. A malfunctioning EGR system can lead to elevated emissions and, consequently, trigger Fault Code P0420. Addressing any identified issues within the EGR system is crucial for resolving the code and maintaining emission control efficiency.
Advanced diagnostics and testing provide a more thorough understanding of the factors contributing to Fault Code P0420. By leveraging specialized tools and tests, mechanics can pinpoint intricate issues, enabling precise and effective solutions. In the subsequent sections, we will explore strategies for resolving P0420 based on the diagnostic findings, ensuring a comprehensive approach to restoring the vehicle’s emission control system to optimal functionality.
Addressing and Resolving P0420 Fault Code
A. Repairing or Replacing a Failing Catalytic Converter
If diagnostic tests confirm a failing catalytic converter as the cause of Fault Code P0420, repair or replacement is essential. Repair may be possible for certain issues, such as minor damage, but a severely degraded or damaged converter may require replacement. Choose a compatible and high-quality catalytic converter to ensure optimal performance and compliance with emission standards.
B. Replacing Faulty Oxygen Sensors
Faulty oxygen sensors contribute significantly to the triggering of P0420. Replace any identified malfunctioning oxygen sensors to restore accurate data transmission to the OBD-II system. Ensure that the replacement sensors meet the manufacturer’s specifications to maintain proper air-fuel mixture monitoring and prevent the recurrence of the fault code.
C. Fixing Engine Misfires and Addressing Fuel System Issues
Engine misfires and fuel system issues can disrupt the combustion process, leading to increased emissions and triggering P0420. Address misfires promptly by replacing spark plugs, ignition coils, or other components contributing to the issue. Additionally, inspect and repair any fuel system issues, such as faulty injectors or a malfunctioning mass air flow sensor, to ensure a balanced air-fuel mixture.
D. Repairing Exhaust System Leaks
Exhaust system leaks introduce excess oxygen into the system, impacting the catalytic converter’s performance and triggering P0420. Identify and repair any leaks in the exhaust system promptly. This may involve fixing damaged pipes, replacing gaskets, or addressing issues with the manifold. Thoroughly inspect the entire exhaust system to ensure all potential sources of leaks are identified and addressed.
E. Clearing the Fault Code and Retesting the Vehicle
After completing the necessary repairs and replacements, use an OBD-II scanner to clear the Fault Code P0420 from the system. This step is crucial to ensure that the repairs have effectively resolved the underlying issues. After clearing the code, conduct a retest by driving the vehicle under various conditions to allow the OBD-II system to monitor the components and verify that the fault has been successfully addressed.
By systematically addressing and resolving each identified issue, vehicle owners and mechanics can effectively eliminate Fault Code P0420 and restore the optimal functionality of the emission control system. Regular maintenance and proactive measures to address emerging issues contribute to sustained vehicle performance and compliance with emission standards.
Preventive Measures and Maintenance
Regular Inspection and Maintenance of the Exhaust System
Implementing a routine inspection and maintenance schedule for the exhaust system is crucial in preventing the recurrence of Fault Code P0420. Regularly examine the catalytic converter, exhaust pipes, and manifold for signs of wear, corrosion, or damage. Addressing minor issues promptly can prevent them from escalating into more significant problems, contributing to the overall health of the emission control system.
Scheduled Replacement of Oxygen Sensors and Catalytic Converters
Oxygen sensors and catalytic converters have a finite lifespan and play vital roles in emission control. Implement scheduled replacements for these components based on the manufacturer’s recommendations. This proactive approach ensures that these critical elements are functioning optimally, reducing the risk of triggering Fault Code P0420 due to sensor or converter degradation.
Using High-Quality Fuel and Addressing Engine Issues Promptly
The quality of fuel directly impacts the combustion process and, consequently, the performance of the catalytic converter. Use high-quality fuel to minimize the buildup of deposits and contaminants in the engine and exhaust system. Additionally, address engine issues promptly, such as misfires or fuel system problems, to prevent the occurrence of Fault Code P0420. Regular maintenance and prompt resolution of emerging issues contribute to sustained fuel efficiency and emission control.
Conclusion
Recap of the Significance of Fault Code P0420
In conclusion, Fault Code P0420 serves as a critical indicator of potential issues within the catalytic converter and the overall emission control system. It highlights the importance of maintaining a well-functioning exhaust system to ensure compliance with emission standards and reduce the environmental impact of vehicle emissions.
Importance of Timely Diagnostics and Repairs
Timely diagnostics and repairs are paramount when dealing with Fault Code P0420. Ignoring or delaying the resolution of this code can lead to increased emissions, decreased fuel efficiency, and potential damage to essential components. Swift action based on accurate diagnostics ensures the efficient and cost-effective resolution of the underlying issues, promoting the longevity and reliability of the vehicle.
Encouraging Regular Vehicle Maintenance to Prevent Future Issues
Encourage regular vehicle maintenance as a proactive measure to prevent future issues. Routine inspections, adherence to scheduled component replacements, and prompt resolution of emerging problems contribute to the prevention of Fault Code P0420 and other potential issues. Investing in preventive measures not only ensures a smoother driving experience but also extends the lifespan of the vehicle while minimizing repair costs.
By adopting a proactive approach to vehicle maintenance and addressing potential issues promptly, vehicle owners can mitigate the risk of encountering Fault Code P0420 and contribute to a cleaner and more sustainable driving environment.
FAQ
Q1: What is Fault Code P0420?
A1: Fault Code P0420 is a Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) that indicates a potential issue with the catalytic converter in a vehicle’s exhaust system. It is triggered when the OBD-II system detects inefficiencies or malfunctions affecting the converter’s performance.
Q2: What are the common causes of P0420?
A2: Common causes of P0420 include aging or failing catalytic converters, malfunctioning oxygen sensors, engine misfires, exhaust system leaks, and fuel system issues leading to an incorrect air-fuel mixture.
Q3: How can I diagnose P0420?
A3: Diagnosing P0420 involves using an OBD-II scanner for code retrieval, interpreting freeze frame data to identify triggering conditions, visually inspecting the exhaust system, testing oxygen sensors, and checking for exhaust leaks or misfires.
Q4: How do I address P0420?
A4: Addressing P0420 involves repairing or replacing a failing catalytic converter, replacing faulty oxygen sensors, fixing engine misfires, repairing exhaust system leaks, and clearing the fault code after completing necessary repairs.
Q5: How can I prevent Fault Code P0420 in the future?
A5: Preventive measures include regular inspection and maintenance of the exhaust system, scheduled replacement of oxygen sensors and catalytic converters, and using high-quality fuel. Address engine issues promptly to maintain optimal emission control.